Standard operating procedure (SOP) for change control management. Change Control Procedure is a formal controlled documented process by which qualified representatives from appropriate discipline, review, propose and make changes to an approved system.
SOP for Change Control Management
1.0 PURPOSE:
-
- This standard operating procedure defines the requirements to ensure changes to systems (includes equipment and utilities), products, processes, procedures, and documents that could impact product quality/compliance are evaluated, documented, and approved prior to implementation and closure.
2.0 SCOPE:
-
- This SOP applies to, but is not limited to changes that could impact:
-
- Product quality, including introduction or discontinuation of product, activities prior to commercial batches of product and/or scale-up, and changes to facilities.
-
- Product Shelf life extension/reduction.
-
- For production, packaging, labeling, and specifications/ intermediates shipped as final drug products.
-
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP), specification/methods for biological products, analytical test procedure / analytical templates, stability protocol/stability templates.
-
- Approved validation document, (validation master plan, cleaning validation master plan, process validation master plan, analytical method validation master plan, and equipment qualification master plan).
-
- Planned preventive maintenance of equipment or instrument or exchange of like-for-like components during servicing.
-
- Any modification, which is planned for the alteration, deletion, and up-gradation, and repair, replacement of equipment, facility, area, or utility
-
- Materials, utilities, equipment, instruments, (including utilities, applications and infrastructure components such as network, servers and client workstations), engineering drawings, design, made by the pharmaceutical manufacturing unit.
3.0 REFERENCES:
-
- Risk Management SOP
-
- SOP for Corrective/Preventive Action Recommendation
4.0 RESPONSIBILITY:
-
-
Quality head/designee shall be responsible for :
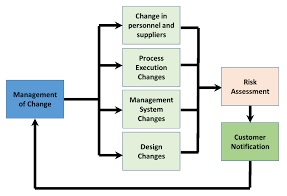
- Implementing and managing a system for the change control process.
-
-
- Ensuring all aspects of the change control process, including management of change proposals, change evaluations, change approvals, change implementations, and effectiveness checks of change(s).
-
- Obtaining the necessary information from other organizational units to comprehensively evaluate the potential impact of the change(s) on other sites” processes, as appropriate.
-
- Provide the notification of changes to regulatory affairs (RA), FDD, PDD, ADD, customers, and market representatives.
-
- Changing classifications. (e.g. Level I, II & III).
-
- Establishing and maintaining procedures to assure the proposed changes to a system are evaluated for potential impact on the following:
-
-
Documents (examples include, but are not limited to):
- Standard operating procedures,
- Quality agreements,
- Training requirements,
- Specifications,
- Analytical Methods,
- Analytical templates,
- Worksheets,
- Master Batch records,
- Master packaging record,
- Quality manual,
- Protocols,
- Labeling,
- Methods used in manufacture,
- Packaging, Testing, release, and distribution of products,
- Manufacturing/packaging instructions, including regulatory commitments for global processes, cGMP engineering drawings.
-
Product characteristics (examples include, but are not limited to):
- Microbial testing,
- Identity,
- Quality,
- Strength,
- Purity,
- Safety and
- Efficacy of Drug Products.
-
-
-
Validation (examples include, but are not limited to):
- Process,
- Equipment,
- Facilities,
- Critical utilities,
- Testing analytical methods (chemical, physical, microbiological),
- Cleaning.
-
-
-
Materials/Supply chain (examples include, but are not limited to):
- Change in the source of any raw material or primary packaging, material/printed packaging material,
- Change in primary packaging material of raw materials,
- Suppliers/vendor’s manufacturing location/process changes,
- Change in the origin of the material.
-
-
-
Initiator/responsible person (RP) of a Change Control Record (CCR) shall be responsible for :
-
-
- Defining, discussing, and documenting objectives, scope, and deliverables of Change Control Record (CCR) with stakeholders.
-
The initiator of a Change Control Record/request shall be responsible for :
- Initiating the Change Control Record and ensuring that change is implemented in accordance with this procedure and managing the implementation activities in accordance with stakeholders’ review comments and agreed action items.
-
- Managing timely execution of activities in conjunction with the stakeholders and Completing risk assessments.
-
- Adding action items as required.
-
- Resolving issues, if any, in coordination with stakeholders and Quality Assurance (QA). Escalating issues, such as extensions of Change Controls not being closed in a timely manner to higher management whenever required.
-
- Initiating variation proposal(s) such as changes being effective (CBE) via CCR, if required, based on CCR evaluation done by regulatory affairs (if required).
-
- Ensuring that all necessary activities related to the implementation of change, including performing a risk assessment of the change are satisfactory and verified.
-
- Responsible for discontinuing Change Control Records, as appropriate.
-
Initiator’s head of department (HOD)/designee shall be responsible for :
- Reviewing proposed change with reference to its impact on systems and procedures; approving the proposed change and ensuring that the change is executed according to identified implementation activities.
-
- Ensuring the tracking of change-related activities and closure of change control.
-
-
Regulatory affairs (RA) head/designee shall be responsible for :
-
-
- Reviewing the proposed change with reference to regulatory impact.
-
- Communicating the change to the Regulatory Agency/Customer (if applicable) via a variation (CBE, Prior Approval Supplement (PAS) as examples) or annual report.
-
- Change Control Record evaluator(s) shall be responsible for reviewing the proposed change for possible impact on systems and procedures from respective disciplines, such as process development, validation or material/vendor sourcing.
-
-
Quality Assurance (QA) head/designee shall be responsible for :
- Approving or rejecting the proposed change with respect to the impact on quality/GMP compliance.
-
-
- Ensuring the adequacy of action items, approving the Change Control Record, assigning the change level classification (I, II, & III) to the CCR.
-
- Performing impact and risk assessment, Identifying and generating action items, as required.
-
- Approving the extension of Change Control Record closure, Performing document assessment, closure of all action Items, and Performing Trend Analysis of Changes.
5.0 ABBREVIATIONS USED IN CHANGE CONTROL SOP:
-
- ADD: Analytical Development Department
- API: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient
- BOM: Bill of Material
- CAPA: Corrective and Preventive Action
- CCR: Change Control Record
- cGMP: Current Good Manufacturing Practice
- CMO: Contract Manufacturing Organization
- CQ: Corporate Quality
- DCGI: Drug Controller General of India
- EHS: Environment Health and Safety
- FDD: Formulation Development Department
- FP: Finished Product
- HACCP: Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points
- LIMS: Laboratory Information Management System
- PCRR: Post Change Review Requirement
- PDD: Packaging Development Department
- SISPQ: Safety, Identity, Strength, Purity, and Quality
- SMF: Site Master File
- STC: Site Training Coordinator
- VMP: Validation Master Plan
6.0 DEFINITION – CHANGE CONTROL MANAGEMENT:
-
-
Action Item Record:
- A record used to document the initiation, execution, verification, and closure of action items generated during a change control process.
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API):
- An ingredient intended to furnish pharmacologic activity or other direct effects in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease or to affect the structure or any function of the body; it does not include intermediates used in the synthesis of such an ingredient.
-
Corrective and Preventive Action:
- A concept with current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) that focuses on the systematic investigation of root causes of unexpected incidences to prevent their recurrence (corrective action) or to prevent their occurrence (preventive action).
-
Corrective Action:
- Action is taken to eliminate the causes of an existing nonconformity, defect, or other undesirable situation, in order to prevent a recurrence.
-
Preventative Action:
- Action is taken to eliminate the cause of a potential nonconformity, defect, or other undesirable situation, in order to prevent occurrence.
-
Change:
- The creation, revision, or discontinuance of a process, software, equipment, facility, utility, product, or document.
-
Contract Manufacturing Organization:
- An organization that supports any part of or completes the process of manufacturing, labeling, packing, testing, and distribution of products on behalf of another organization. Contract manufacturing involves the production of goods by an organization, under the label or brand of another organization.
-
Critical cGMP Engineering Drawing:
- A drawing that is representative of a piece of equipment, part, building, or flow of material/personnel that provides information concerning the attributes or characteristics of the equipment, part, building, or flow of material/personnel. (Note: A change to the equipment, part, building, or flow of material/personnel could impact the identity, strength, or purity of the product being manufactured, packaged, held, or tested.
-
Cross-Functional Team:
- A group of people with different functional expertise working towards a common goal. The team is responsible for the review and implementation of the Change Control Record.
-
cGxP :
- cGxP is a general term that stands for current Good “x” Practice (x = Clinical, Engineering, Laboratory, Manufacturing, Documentation, Pharmaceutical, etc.).The titles of these Good “x” Practice guidelines usually begin with “Good” and end in “Practice”. cGxP represents the abbreviations of these titles where “x” a common symbol for a variable, represents the specific descriptor.
-
Global Product/Process:
- Products/processes that are manufactured, packaged, tested and/or distributed in multiple countries and that require individual registrations.
-
Initiator:
- An individual who initiates the Change Control Record and/or Action Item Record.
-
Like-for-Like Change:
- This term is applicable to the replacement of components on equipment. A change where the same specifications are met (e.g. size, rate, horsepower, voltage, materials of construction) between the current state and proposed state. Typically, the manufacturer and model number are identical and for product-contacting surfaces, materials of construction are identical. Like-for-like change documentation, including QA approval, demonstrates that functional requirements are met.
-
Minor Change – Level I:
- A minor change is a change that has minimal potential to have an impact on the identity, safety, strength, quality, purity, and efficacy of the product or validation status of the process, equipment, utility, facility or GMP compliance/procedures, and systems or regulatory filings.
-
Moderate Change – Level II:
- A moderate change is a change that has a moderate potential to have an impact on the identity, safety, strength, quality, purity, and efficacy of the product or validation status of the process, equipment, utility, facility or GMP compliance/procedures, and systems or regulatory filings.
-
Major Change – Level III:
- A major change is a change that has a substantial potential to have an impact on the identity, safety, strength, quality, purity, and efficacy of a product or validation status of the process, equipment, utility, facility or GMP compliance/procedures, and systems or regulatory filings.
-
Quality Management System:
- Business processes focused on achieving quality policy and quality objectives to meet customer requirements. It is expressed as the organizational structure, policies, procedures, processes, and resources needed to implement quality management
-
-
- Responsible Person: An individual responsible for the completion of Action Items.
-
-
Variation:
- A documented notification (e.g. Changes being Effected (CBE), Prior Approval Supplements (PAS), Annual Product Reports (APR)) to be filed with a Regulatory Agency informing them of a change that has an impact on the company’s registered documentation available with the Agency.
-
Variation Management:
- Tasks created for capturing the variation dossiers submission/filing dates to the various Regulatory Agencies and tracking the Agency approval/rejection status of the variations.
-
Definition of Change Control:
- A formal system by which qualified representatives of appropriate disciplines review proposed or actual changes that might affect a validated status. The intent is to determine the need for action that would ensure that the system is maintained in a validated state.
-
-
- Change control procedure: A formal controlled documented process by which qualified representatives from appropriate discipline, review, propose and make changes to an approved system.
-
- Corrective Action: Action to eliminate the cause of a detected nonconformity or other undesirable situation.
-
- Control system: Is a planned set of control, derived from current product and process understanding that assures the process performance and product quality. The controls include parameters and attributes related to drug substance and drug products, materials and components, facility and equipment, operating conditions, in-process controls, FP specifications, storage/shipping conditions, and associated methods as well as the frequency of monitoring and control.
7.0 PROCEDURE FOR HANDLING OF CHANGE CONTROL:
-
-
Initiation of change control record (CCR):
- The Initiator shall discuss the proposed change with the Department Head and key stakeholders, including, but not limited to, Quality Assurance and Regulatory Affairs to reach a consensus that the change is necessary, feasible, and supportable whenever required.
-
-
- Once the agreement is reached regarding the proposed change, the Initiator shall initiate a Change Control Record (CCR).
-
- QA shall issue the Change Control Record to the concerned department & shall assign the change control number on the form with signature and date for issuance.
-
- Simultaneously QA shall fill the CCR details in the change control logbook. Fill the details of the CCR as per Annexure 1 – CHANGE CONTROL RECORD.
-
SECTION A: (Filling of Change Control Form – Annexure 1)
- Change Control Number: QA shall assign a unique identification number (change control number) to each change control Record and make necessary entries in the change control record Annexure 1 – CHANGE CONTROL RECORD.
-
- QA shall assign the change control number as per the below-mentioned procedure.
- Change control number shall be alphanumeric i.e. CC/XX/ZZZ.
- Where –
- CC stands for Change Control
- XX stands for the Last two digit of the current year (for the year 2020, “20”)
- ZZZ stands for serial no. (Start from 001)
-
- Change control number shall be item dependent and serial number will run in continuation irrespective of the item.
-
- Date of issuance: The date on which the change control number is assigned, shall be written by QA.
-
- Provide the change category (e.g. batch size change, composition change, etc.).
-
- Based on the type of change, document/product details shall also be included in the change control record.
-
- The initiator shall also give details for the proposed change category in the change information section(s).
-
- Target completion date: QA shall mention the Target completion date in consultation with the concerned department.
-
-
Timeline for Closure of Change Control Form :
- Change control shall be closed within 90 days from its approval date, however, the concerned department shall take the extension date as per Annexure 8 – Justification For Change Control (if required).
-
-
- Justification for extension shall be practical as well as logical. Supporting data if required and shall be attached to Annexure 8 – Justification For Change Control.
-
- QA shall track the open change controls while issuing new change control to the initiating department. New change control shall not be issued if similar change control is already available at any stage of implementation.
-
-
Title of change:
- A suitable title for the proposed change shall be written in this column. The same shall be written in logbook too.
-
-
- Previous change control number (if any): At the time of change control form issuance QA shall identify any previous change control raised for the same product and same reason.
-
- Initiated by: Write the name of the person to whom the change control is issued.
-
- Department: Initiator shall mention the name of her/his Dept. in the respective places.
-
- Logged by: The QA person who is issuing the change control shall put his/her initial.
-
- After making all relevant entries into the Change control record, QA shall write the relevant information in the change control register (Annexure 2 – Change Control Register) and issue the CCR to the initiator.
-
- For new/transferred product introduction shall be handled as per SOP of Technology Transfer of Drug Products.
-
- For discontinuation of the product, impact evaluation shall be done as per the checklist is given in Annexure 9 – Checklist For Discontinuation Of Product.
-
-
Product/Material Name/Document Name/ SOP title:
- The initiator shall mention the details related to the product name/ material name/document name / SOP title for which the change is initiated.
-
Batch No. /A.R No. /Document No.:
- In case of change, Batch no. of the Product or A.R. No. of Material for which the change is initiated shall be written. In case of permanent change, document no. shall be written by the initiator.
-
-
- Existing System: Initiator shall mention the details of the existing process/formula/procedure/equipment or Specification that is being followed.
-
- Proposed Change: Initiator shall mention the details of the proposed process/formula/procedure/equipment or specification that is to be followed.
-
- Reason/Justification: Initiator shall mention the clear reason for change initiated along with justification based on supporting data like history, trend, stability data or ADD/FDD documents, scientific rationale, event/audit observations, and experience or any other to ensure no adverse impact on product quality.
-
- After filling in the change details, the initiator shall put his/her signature along with the date and submit the completed Change Control Record to his /her dept. head for review and comment.
-
- The Initiator’s Department Head shall review and provide comments, as necessary, and may either approve, seek additional information/changes or not approve the Change Control Record with comments.
-
- If additional details/information is asked for by the Department Head, the Initiator shall make necessary changes to the proposed change and shall, again, submit the Change Control Record to the Department Head with the additional information.
-
- After initiator department head review and approved Change Control Record shall be given to QA. CCR initiator who after consultation with QA head or designee shall provide CCR number.
-
- The Department Head shall review and shall initiate an Action Item Record, as needed and as explained in section 2. The Department Head shall then approve the Change Control Record and submit to the QA Designee for review and evaluation.
-
-
In case the space provided in the change control form is not sufficient to accommodate the changes, details shall be mentioned on separate sheet/s in Annexure 5. (Annexure 5 – Change Control Annexure).
-
-
- Annexure 5 (Annexure 5 – Change Control Annexure) can be customized to meet the requirements for producing support data/justification for change control approval.
-
- In case any amendment is required to the initial change control record, which has been approved and not yet implemented or under implementation; the initiator shall fill another Annexure 5 and follow the change control management.
-
- Initial change control reference number shall be applicable which will indicate as an addendum to the original change record.
-
- In case, during implementation, additional changes are identified, which are the minor changes, and then the same shall be mentioned in separate annexure 5 prior to implementation, the same shall be discussed with QA Head.
-
- Incase, identified changes are major changes, then the same shall be implemented by following the addendum procedure as described above. The same shall also be mentioned in the revision history of the impacted document(s).
-
- The addendum change request details also are logged as per prescribed procedure as followed in case of fresh change control requests.
-
- All addendum change requests along with the original change control shall be closed after ensuring the implementation of final proposed changes.
-
- In case of a change initiated for one document which may impact other documents (s), the respective document(s) can be revised with reference to the same change control initiated for mother change.
-
Section B (Filling of Change Control Form – Annexure 1) :
- Impact Analysis of the Change Control Record:
-
- The QA designee shall
- Evaluate the Change Control Record based on the Risk/Impact Assessment and proposed a mitigation plan submitted by the initiator to decide whether to process the CCR further and return comments to the initiator accordingly.
- The QA designee shall
-
-
- May seek additional information or cancel the proposed change with justification.
-
-
-
- Mention the impacted items by writing Yes / No in the column as per Annexure 4 – Impact Analysis.
-
-
- Impacted department Head / Designee shall provide recommendations in impacted items followed by their sign/date for impact analysis to support ultimate output. (Refer Annexure 4 – Impact Analysis.).
-
- Risk Assessment: Risk assessment to be performed as per SOP of risk management. if suggested by the concerned department.
-
- CAPA: Quality Assurance shall issue CAPA for long-term corrective action and preventive action(s) to the concern impacted Dept. Head to monitor the recommendation/s as applicable. The CAPA shall be issued based on the discretion of the QA Head/Designee.
-
- The “Department Selection Matrix for Change Control Evaluation” based on the type of change shall be detailed more specifically in Annexure 10 – Department Selection Matrix. Few examples are given for reference purpose:
-
Process Technology Development (PTD)/Technology Development (TD)/ Manufacturing Science and Technology Group (MSTG)/User Department:
- Introduction of new product (e.g. different strength / combination / market/dosage form, etc.) at site.
-
- Raw materials/primary packaging materials in the drug product.
-
- The supplier’s process changes that may affect the form, function or quality of the product.
-
- Change in manufacturing formula, process or control parameters, labeling and addition of any new product (e.g. different strength/combination/market/dosage form) in existing facilities.
-
- Change in master documents Formulation Order (FO) and Manufacturing Instructions (MI)/Packaging Order (PO) and Packaging Instructions (PI).
-
- Recipe linkages change.
-
- Artwork Changes.
-
Production/User department:
- Equipment Change (introduction/discontinuation/movement of equipment).
-
- Process and process control parameters changes.
-
- Cleaning procedures changes or changes in batch size.
-
- Change in BMR (Batch Manufacturing Record)/BPR (Batch Packaging Record) and MPR (Master Production Record).
-
- Container closure changes.
-
- Change in facility/manufacturing sites.
-
- Change in manufacturing equipment and related software.
-
- Expansion or modification of the Production area.
-
- Interchangeability of equipment (e.g. agitator).
-
Warehouse/ User department:
- Equipment changes (introduction/discontinuation/movement of equipment).
-
- Change in the material receipt and storage area.
-
- Change in tank farm area (solvent storage area).
-
- Sampling booth/area change.
-
- Storage area change.
-
Materials/Supply Chain/ User department:
- Change in the source of any raw material or primary/secondary packaging materials/printed packaging materials.
-
- The primary packaging material of raw materials Change.
-
- Change in vendor/manufacturer.
-
- Change in suppliers/vendor’s manufacturing location/process.
-
Engineering/ User department:
- Installation of new equipment.
-
- Change in any critical equipment or its critical part or control parameters in utilities, facilities.
-
Planning/ User department:
- Change in batch size and product site transfer.
-
Quality Assurance/ User department:
- Change in sampling procedure and product shelf life.
-
Quality Control/ User department:
- Change in QC instruments and related software.
-
Information Technology/ User department:
- Changes in Computer System post-implementation during the life cycle, e.g. Changes in application of enterprise software solutions, e.g. Systems, Applications and Products in Data Processing (SAP), CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) Quality Management System (e.g. Trackwise)
-
Environment, Health, and Safety/ User department::
- Responsible for evaluating the impact on Hazard and Operability study (HAZOP), Environmental aspects, etc.
-
- The initiator of the Change Control Record shall submit the CCR to site EHS department for review, evaluation, signing and for recommending impact analysis. (Annexure 12 -Check List For EHS Impact Evaluation)
-
- Depending on the modification, the EHS department shall use the checklist for doing Impact Evaluation.
-
- If there is no impact is evaluated accordingly it shall be mentioned in the PMF form.
-
- Attach the checklist to the Change Control Record.
-
- EHS head shall review the completion of all recommendations.
-
- Details of changes shall be explained by the change control initiator to the concern evaluated department via change information form (Annexure 7 – Change Information Form) or by conducting training as recommended in Annexure 10 (Annexure 10 – Department Selection Matrix). The concerned person shall execute the change in coordination with QA & shall prepare assessment reports/data.
-
- After the recommendation of the impacted Dept., impact analysis shall be done by change control initiating department head and reviewed by QA Head / Designee.
-
Creation of action item record:
- The Initiator/Evaluator(s)/QA, during the review of the Change Control Record, shall create Action Item records.
-
- Each Action Item record shall be assigned a unique identification number.
-
- Action item number shall be action dependent of reference Change Control Record and serial number will run in continuation with an irrespective action item.
-
- The Initiator, after opening an Action Item record, may cancel the record and shall include justification documentation in the record supporting the cancellation.
-
- The initiator shall complete the action item activity and forward documentation to another person in the initiator department for verification QA and after that QA shall perform the verification activity.
-
- If verification is not satisfactory, QA shall notify the initiator with documentation concerning the verification failure.
Also read: SOP for Vendor Management
-
- If verification is satisfactory, QA Designee may take the following action:
- Close the Action Item record.
- If verification is satisfactory, QA Designee may take the following action:
-
-
- If not satisfactory, send the Action Item record back to the Initiator with justification.
-
-
Section C (Filling of Change Control Form – Annexure 1) :
-
Approval for Execution of the Change Control Record:
- If the proposed change is to be processed further, the QA Designee shall classify the change as Level I, Level II and Level III, based on the risk to product quality and patient safety.
-
-
- The QA Designee shall then identify the departments to which the Change Control Record needs to be sent for evaluation and approval and shall submit the CCR to the Responsible Person of each identified department.
-
- A guidance list for the selection of departments for evaluation of Change Control Record based on the type of change is given as Annexure 10 – Department Selection Matrix.
-
- Adequacy of impact analysis through recommendation, all Change Control Records shall be approved by Dept. Head / Production Head, Q.A Head and Quality Head. QA Head shall classify the level of Change Control Record.
-
- Change Review Level: The change review level shall be decided by QA Head or Designee based on the following criteria.
Note: If in a change control different changes shall fall under different levels, then based on the maximum level, its approval steps shall be decided.
-
-
Level I:
- No impact on control system ensuring SISPQ of product. e.g.
- Reduction in Hold time,
- Tightening IP / FP limits,
- Increased frequency of monitoring and in-process checks.
-
-
-
Level II:
- The changes do not have a significant impact on the control system however that triggers validation/qualification/stability study etc. e.g.
- Establishment/increase of hold time,
- Introduction of new count / new pack,
- Change in SOP/Template/Protocol/LIMS documents,
- Change in Machine/Equipment,
- Release limit change (e.g. from IH to USP, etc.),
- Change in In-process parameters,
- Change in Pack style/Pack count.
-
-
-
Level III:
- The changes have a potential impact on product quality/regulatory bodies according to respective guidelines i.e Changes except for annual notification requirements. e.g.,
- Change in Calibration/Stability frequency,
- Change in FP limits(Dissolution / Average Wt. etc.),
- Batch size change,
- Updation of pharmacopoeial change,
- Change in the strength of RM (e.g. Pellets),
- Change in Manufacturing formula,
- Relaxation of FP limit,
- Launch of new product/system,
- Change in Storage condition,
- Change in Primary Packing Material,
- Product Shelf Life Extension,
- Deletion, and
- Up-gradation, and repair, replacement of equipment, facility, area, or utility.
-
-
- After making all relevant entries into Change Control Record, QA- shall update relevant information in the CCR register (Annexure 2 – Change Control Register) and give the Change Control Record to the initiator for impact evaluation.
-
- The QA Designee may also initiate an Action Item Record, as needed and as explained in the above section.
Also read: Record Retention and Archival Policy
-
- If the change is not justified, Dept. head or QA Head can reject the change control with proper comments/justification.
-
- If the change control is rejected, then QA can close the change control with a comment as not implemented.
-
- The identified department shall evaluate the Change Control Record for the impact it may have on the systems and procedures linked to the proposed change.
-
- The Checklist is given in Annexure 4 – Impact Analysis. shall be used as a guidance document for impact assessment. Supporting documents shall be attached, wherever applicable.
-
- An Action Item Record, as required and as explained in the above sections, shall be created by the respective Department(s) during the evaluation of the Change Control Record proposal.
-
Section D – (Filling of Change Control Form – Annexure 1) :
-
Action Item Closure Details and Evaluation:
- Impact Evaluation Criteria by department follows:
- Regulatory Approval/Notification Required – State whether regulatory approval/notification is required; if regulatory notification is required, provide appropriate details – which type of submission/filing needs approval, from which Agency and tentative timeline for filing.
-
-
-
- Stability Studies – State whether stability studies are required, provide stability conditions that need testing and the number of batches that need to be charged on stability.
-
-
-
- Validation Studies – State whether validation studies are required based on the type of change; provide details of the type of studies and the scope of the studies.
-
-
- Evaluation of the regulatory impact of the Change Control Record and the need to file a variation with the Agency for the planned change.
-
- Initiate a variation proposal based on the evaluation category or notify the Change Control Record initiator to initiate a variation proposal.
-
- Record comments, if any and attach documents, as needed.
-
- Regulatory Affairs Designee shall also create an Action Item Record, as needed and as explained in section 7.4(if required).
-
- Stakeholders/Cross-Functional Team: Head/Designee/ Members shall evaluate the impact of the change to process validation studies, marketing approval and provide additional inputs, as necessary on the following:
-
-
- Determine if process validation studies are required and provide details of the type of studies and describe the scope of the studies based on current regulatory requirements.
-
-
-
- If market authorization (business approval) is required.
-
-
-
- If there is any impact on the stability of the product/formulation.
-
-
-
- Identify the effect (if any) that the proposed change shall have on each of the following:
- Formulation Order,
- Manufacturing Instructions,
- Packaging Order,
- Packaging Instructions,
- SOPs and Training,
- Artwork,
- Development batch data,
- Computerized control systems/applications.
- Identify the effect (if any) that the proposed change shall have on each of the following:
-
-
-
- Identify updates required to Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing (SAP) data.
-
-
Section E – (Filling of Change Control Form – Annexure 1) :
- Implementation and Change Closure Details:
-
Production:
- Head/Designee shall evaluate the impact of the change to, but not limited to,
- Process/procedure,
- Process equipment,
- Validation or qualification activities or need for area qualification.
Also read: Document Management System
-
-
Quality Control:
- Head/Designee shall evaluate the impact of the change to, but not limited to:
- Analytical Instruments and related software, including Calibration,
- Preventive Maintenance practices and schedules,
- Stability specifications,
- Analytical methods,
- Validation or Qualification activities,
- Environmental Monitoring,
- Raw Material Specifications,
- Packaging Specifications,
- In-Process,
- Finished Product Specifications,
- Analytical Test Method Transfer and Stability studies.
-
Engineering:
- Head/Designee shall evaluate the impact of the change to, but not limited to,
- Process equipment,
- Piping,
- Duct or other facility layouts;
- System capacities or other key equipment/utility parameters;
- Temperature-mapping in the warehouse system and determine.
-
Validation:
- Head/Designee shall evaluate the impact of the change to, but not limited to,
- The validation of process or qualification of facilities,
- Equipment Hold times,
- Cleaning validation,
- Computerized systems and utilities.
-
-
-
Environment, Health, and Safety:
- Head/Designee shall evaluate the impact of the change to, but not limited to, Hazard and Operability Study (HAZOP) and Environmental controls.
-
-
- Once the Change Control Record (Proposal) evaluation is completed by all the stakeholders, comments shall be reviewed by the Initiator. The Initiator shall verify completion of the Action Items initiated and create new Action Items.
Also read: Process Validation SOP and Protocol
-
- After disposition of a variation proposal record, QA shall evaluate the Change Control Record Proposal and Action Items prior to the approval of the proposed change for impact on the validated status of facilities, systems, equipment or processes and shall make one of the following decisions:
- Seek additional information/details or changes and return the Change Control Record to the Initiator.
- Reject the Change Control Record (Proposal) with justification documented and the Change Control Record shall then be canceled and closed.
- Cancel the Action Items initiated by the Initiator/other departments (s) during evaluation with supporting justification
- Identify more Action Items and initiate Action Item records if needed, as explained in the above sections and approve the Change Control Record (Proposal) for implementation.
- After disposition of a variation proposal record, QA shall evaluate the Change Control Record Proposal and Action Items prior to the approval of the proposed change for impact on the validated status of facilities, systems, equipment or processes and shall make one of the following decisions:
Note: The “Checklist for Impact Assessment of Changes”(as per Annexure 4) shall be used as a guidance document for impact assessment and the completed risk assessment record shall be attached to the Change Control Record.
-
- QA shall consult across various departments, as needed, for their suggestions/recommendations before final approval of the Change Control Record.
-
- Approval of Change Control Record shall be communicated to the Initiator, Evaluator(s), the Initiator’s Department Head, Regulatory Affairs and other stakeholders as deemed necessary, including all departments involved in initial approval of the change control, as well as in-process approvals.
-
- Clear all-action Items for implementation only after QA’s final approval of the Change Control Record.
-
- The initiator shall complete all Action Items, as identified during the evaluation of Change Control Record by various stakeholders. Similarly, the stakeholders concerned shall complete actions related to all the child change controls raised as a part of Variations that are the responsibility of and managed by Regulatory Affairs. Child change controls shall follow the same change control process illustrated in the workflow (Annexure 6 – Flow Chart For Change Control Procedure).
-
- During or after the execution of the change implementation activities, the Department Head of the Initiator may propose to discontinue the change proposal with justification documentation to the QA Designee.
-
- If a change discontinues request (Annexure 11-Change Discontinue Request) is approved by QA, the Change Control Record and all related action item(s) and variation proposal (if initiated) shall stand closed.
-
- Change Control Record discontinuances that are denied by QA with appropriate documentation shall remain in effect until closing.
-
-
If the change has not implemented (fully or partially), then change control can be closed with proper justification for non-implementing the changes.
- At the time QA reviews the change discontinue request for approval, the status of action item implementation shall be assessed.
-
-
-
- QA shall determine if action items already implemented are acceptable in view of the Change Control Record discontinuation and if so shall document this in the Change Control Record.
-
-
-
- If the implementation of action items is not acceptable where the Change Control Record is being discontinued.
-
-
-
- QA shall document this in the Change Control Record and include instructions for corrective action to be taken prior to final approval of change discontinue request.
-
-
-
- The Initiator shall ensure satisfactory closure of all identified Action Item(s).
-
-
-
- The QA Designee shall verify satisfactory closure of all Action Item(s) and that appropriate documentation is complete and included.
-
Also read: Technology Transfer of Drug Product
-
- Based on the review of data/assessment report/outcome/results (satisfactory / not satisfactory), QA Head shall make final conclusion, whether the change was implemented successfully or not and write the closure comments accordingly.
-
- During the closure, QA Head shall decide the need for a Post-change review.
-
- If post changes monitoring or impact assessment is required, then QA Head shall recommend the same with a comment.
-
- After this change, control closure can be done and approval from all concerned persons shall be taken by the initiator.
-
- QA shall update the closure details of change control in the logbook and shall archive the form in a safe QA custody for future reference.
-
- QA shall review the logbook on a monthly basis to identify the change control request which needs to be closed or the target date for closure is due.
-
-
Note: In case of extension or reduction of product shelf life, the location shall submit the relevant stability data to CQ for review and approval.
-
-
- CQ shall review and seek an opinion from FDD and if found acceptable shall recommend for extension of shelf life.
-
- The location shall inform RA to initiate the regulatory procedures for a change in the shelf life of the product.
-
- Implementation of a revised shelf life shall through the change control procedure.
-
- Change Control Record shall close once all the Action Items and Variation Proposal(s) implementations (if raised) are verified and found to be satisfactory by the QA Designee and closed as “Closed-Implemented”.
-
- In cases when a filed Variation is rejected by the Regulatory Agency, Close the variation Management record as “Closed-Rejected” and the associated parent Change Control Record shall thereafter close.
-
- In the future, if a decision is made to re-file that Variation, then updates shall be documented/processed on the same Variation Management Record and the parent Change Control Record shall also be reopened to update accordingly.
-
- If action items of a Change Control Record are overdue (e.g. have exceeded the due date of completion that is calculated by the system and is based on the suggested list of action items where the assigned change control due date becomes the expected completion date of action item that will take longest to complete.),
-
- The Change Initiator shall request an extension of the closure timeline for the Change Control with justification supporting extension from QA and shall request an impact assessment regarding delay of change implementation.
-
Section F – (Filling of Change Control Form – Annexure 1) :
-
Post Changes and Effectiveness Monitoring of “change”:
- Evaluation of changes undertaken to confirm after change implementation.
-
-
- Achieve change objectives.
-
- Whether there is any adverse impact on product quality.
Also read: Annual Product Review (APQR / APR / PQR)
-
-
Change Implementation is satisfactory.
-
-
- QA shall assign the Post-change and effectiveness monitoring number as per the below-mentioned procedure.
-
- Based on the comment of post changes impact assessment or effectiveness monitoring comment, QA shall fill the details in the logbook and shall track the same by reviewing the logbook on a monthly basis until its closure.
-
- QA shall perform the evaluation based on the criteria set by the Change Initiator at the time of proposing the change.
-
- Track the due date of impact assessment or effectiveness monitoring of changes from the logbook.
-
- Based on the review of change control details, QA Head shall decide the requirement for impact assessment or effectiveness monitoring.
-
- Post-implementation impact assessment or effectiveness monitoring shall be done by QA in coordination with the initiation department.
-
-
Impact assessment or effectiveness monitoring can be done with the help of a customized protocol.
-
-
- Prepare the customized protocol for post-implementation impact or effectiveness monitoring by detailing the objective, scope, sampling plan, frequency of review, justification of review pattern and finally based on findings, Draw appropriate conclusions.
-
- Generate the Protocol numbering and maintained as per the SOP of the list of lists.
-
- If feasible, this impact assessment or effectiveness monitoring can be clubbed with the trend analysis or APQR for the respective product.
-
- If the change has an adverse impact on product quality, the change objective is not achieved and/or change implementation is not satisfactory, the change control shall be resubmitted to QA for a repeat review and re-evaluation.
-
- Initiate appropriate corrective or preventative actions based on this review (e.g. initiation of another change control, change discontinuation).
-
- If the change has no adverse impact on product quality and the change objective(s) are achieved and the change implementation is satisfactory, the change control shall be closed as “Closed-Implemented”.
-
Trend Analysis of Changes:
- Perform the trend analysis of Changes at pre-designated frequencies (at least annually) by QA, either as a part of Annual Product Reviews/Product Quality Reviews, Site Management Reviews or as a separate activity.
-
- Carry out the analysis of trend on one or more of the following parameters (but not limited to):
-
- Change Classification (Major/Moderate/Minor), Parent molecule of the product, Manufacturing Site, Market/Region, Status of Change (Open/Closed).
-
- Identify any adverse trends and additional action (if needed) and proposed to address the same.
-
- Communicate the results of trend analyses to the Site/Global Quality Review Board.
-
- Review the action plant of all Change Controls having overdue for progress and closure, at least monthly, shall be escalated to Site Quality Review Boards (QRB) through the metrics reporting process and actions shall be initiated, wherever needed, for the closure of overdue action items.
-
Requirements:
- Quality Assurance shall assure a comprehensive evaluation of the change is performed by the functional group with the requisite knowledge, training, and experience prior to deciding if the change can be approved for implementation.
-
- Like-for-Like changes do not require a change control as long as these are documented according to a Site Quality Assurance procedure.
-
- Functional groups approving changes shall review and approve the entire change proposal. Site Quality Assurance shall be the final approver.
-
- When a change request is not approved, the functional group that did not approve the change request shall document the rationale for this decision.
-
- Quality Assurance shall communicate to Regulatory Affairs any proposed changes to in-process activities and finished products or APIs that may affect the registration.
8.0 ANNEXURES:
Guidelines For Change Initiation



Pingback: Artwork Management Procedure - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Biological Safety Cabinet - Qualification - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Quality Agreement Technical (Contract Manufacturing) - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: 21 CFR Part 11 : Electronic Records & Signatures - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: SOP for Audit Trail Review and Privilege Policy - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: SOP for Quality Risk Management (Guideline ICH Q9) - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Internal Audit (Self Inspection) Checklist and Format :Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Biosafety Cabinet (ESCO) Operation & Qualification - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Vendor Management - SOP and Complete Guide - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Good Documentation Practices - SOP & Guideline - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: SOP - Corrective Action and Preventive Action (CAPA) - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: SOP for Isolation and Identification of Microorganisms - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: SOP for Drug Product Recall & Mock Recall - Pharma Beginners