 A document is a physical or digital representation of a body of information designed with the capacity (and usually intent) to communicate. Below the Standard Operating System (SOP) for Document Management System.
A document is a physical or digital representation of a body of information designed with the capacity (and usually intent) to communicate. Below the Standard Operating System (SOP) for Document Management System.
A document may manifest symbolic, diagrammatic or sensory-representational information. Following are some examples, but not limited to.
SOP for Document Management System
1.0 PURPOSE:
-
- The purpose of this SOP (Standard Operating Procedure) is describe the procedure for the
- Issuance,
- Handling,
- Archival,
- Destruction and
- Establish requirements for the life cycle management of all cGxP, Regulatory Documents & Records associated with a product, activity or process.
- The purpose of this SOP (Standard Operating Procedure) is describe the procedure for the
2.0 SCOPE:
-
-
This procedure is applicable to
- All documents like -logbooks, BMR, BPR, Site master file and records etc.
-
-
-
- Documents that are associated with all cGxP and Regulatory Documents & Records used in manufacturing, packaging, testing, storage, and distribution of Drug Products.
-
-
- This also applies to documents generated by Pre-Clinical, Clinical and Non-Clinical Studies, Pre-validation Batches, Registration Batches/Exhibit Batches, and Product Development.
-
This procedure is not applicable for –
- Personnel records (except for training records, medical records, attendance records, transfer letters, and sample signature records).
-
-
- Business records pertaining to company sales, marketing or finance that have no impact on cGxP.
-
-
-
- In the case of electronic records, retention of “back-up” data is excluded from the purview of this SOP.
-
3.0 RESPONSIBILITY:
-
-
Site document coordinator shall be responsible for
- Ensuring maintenance of the Document storage room.
-
-
-
- Receiving documents for storage and arranging for systematic archival.
-
-
-
- Maintaining/updating the document log for retention details and retain documents as per the respective retention procedure by site document coordinator.
-
-
-
- Ensuring that the documents and records are retained through established retention timelines comes under the responsibility of the site document coordinator.
-
-
-
- Receiving approved document/record destruction hold notifications from Responsible Persons, then updating the document retention logs and distributing the destruction hold notifications to stakeholders.
-
-
-
- Reviewing the retention dates for documents periodically but not less than annually and arranging for destruction of documents that have met their retention requirements and are not on legal “hold”, in the presence of QA Head.
-
-
-
- Ensuring periodic reviews of Record Retention Schedule.
-
-
-
- The site document coordinator shall responsible for training to employees on the records management program.
-
-
-
Department head/ Designee of document coordinator
- Ensuring the verification of document destruction records are prepared by the Document Coordinator and also adherence to the Retention Period as defined in this procedure.
-
-
-
Regulatory affairs department or designee shall be responsible for
- Providing information for holding the destruction of documents and records which are under quality/legal / regulatory evaluation or review or ongoing litigation.
-
-
-
- Reviewing and approving “Destruction Hold” notifications and forwarding to Document Coordinator.
-
-
-
QA shall be responsible for
- Reviewing / approving Destruction Hold notifications and then forwarding to Document Coordinator.
-
-
-
- Approving the destruction of documents/records that have completed the retention period.
-
-
-
- Ensuring the verification of document destruction records prepared by the document coordinator.
-
Company employees, contractors, consultants, and temporary employees are responsible for
- Complying with record management procedures, company retention schedules and policies.
-
Managers (any employee with direct reports) shall be responsible for
- Ensuring that reporting employee’s records are reviewed by their manager when the employee leaves the company or transfers within the company to prevent “orphan” files.
-
QA head/ designee shall be responsible for
- Managing investigations and impact assessments for event/incidents concerning GDP procedures.
-
-
-
- Authorize the “Document / Record issuance, retrieval Form” and handle deviations observed in the GDP in consultation with the QA team.
-
-
-
Document coordinator shall be responsible for
- Generate, retain documents/records, arrange the documents in an orderly fashion, affix the identification label on file and on the respective shelves.
- Arrange all documents/records in the record room, perform the documentation activities as explained in this guideline.
-
Issuing person shall be responsible for
- Issue the document after making necessary entries in respective registers of Record room / Document Room.
-
4.0 ABBREVIATIONS:
-
- AR. No. : Analytical Report Number
- ACC : Accelerated Condition
- ANDA : Abbreviated New Drug Application
- BMR : Batch manufacturing record
- BMS : Building Management System
- BPR : Batch Packing Record
- CAPA : Corrective and Preventive Action
- COA : Certificate of Analysis
- DC : Document Coordinator
- Doc No. : Document Number
- Exp : Expiry
- GDP : Good Documentation Practices
- GMP : Good Manufacturing Practices
- Mfg : Manufacturing
- NA : Not Applicable
- OOS : Out Of Specification
- OOT : Out of Trend
- QA : Quality Assurance
- QC : Quality Control
- SOP : Standard Operating Procedure
5.0 DEFINITION OF TERMS USED IN DATA MANAGEMENT SYSTEM:
-
-
Active Storage:
- A storage location that is typically on-site and is in the immediate vicinity of the area of use of the documents/records.
-
-
-
- Documents/records that need to be frequently used by the users are usually stored in Active Storage.
-
Inactive Storage:
- A storage location that is typically off-site or one that is not in the immediate vicinity of the area of use of the documents/records is called Inactive Storage.
-
-
-
- Documents/records that have a diminished use and those whose storage at a remote location does not impair normal business are usually stored in Inactive Storage.
-
Archival:
- Data archival is the process of moving data that is no longer actively used, to a separate data storage device for long-term retention.
-
-
-
- The Data archives exist of aged data that is still useful and necessary for future reference, as well as data that must be retained for regulatory compliance.
-
Area / Facility Life cycle:
- The time from project-startup up to permanent shut down of operations in the facility/area or up to de-commissioning of facility/area or up to the expiry date of the last batch produced in the facility/area, whichever is longer.
-
Back-up:
- A backup or the process of backing up is generating copies of data or records to be used to restore the original after a data loss event.
-
-
-
- Backups have two distinct purposes.
-
-
-
- The basic aim is to recover data after its loss, be it by data deletion or corruption.
-
-
-
- The secondary requirement of backups is to recover data from an earlier time, as per the user-defined data retention policy, typically configured within a backup application for how long copies of data are required.
-
Computer System Life cycle:
- An approach to Computer Systems that begins with…
-
-
-
-
- Identification of user requirements;
-
-
-
-
-
- Continues through design,
-
-
-
-
-
- Integration,
-
-
-
-
-
- Qualification,
-
-
-
-
-
- Validation,
-
-
-
-
-
- Control and maintenance; and
-
-
-
-
- It ends only when the commercial use of the system is discontinued and it is retired/decommissioned.
-
Destruction Hold:
- Withholding from destruction documents or records that are under quality/legal / regulatory evaluation or review or ongoing litigation.
-
Record:
- Any document (written, electronically captured or copied) detailing events and actions relevant to the cGxP activity.
-
-
-
- Examples of Records:
-
-
-
-
- Maintenance histories,
-
-
-
-
-
- Change control records,
-
-
-
-
-
- Stability reports,
-
-
-
-
-
- Batch records, etc.
-
-
Reports:
- Report are those documents that generated due to particular exercises, projects or investigations together and consist of results, conclusions, and recommendations.
-
Retention Period:
- The period for which Documents and Records shall be retained/preserved in a facility.
-
Concerned Person:
- Concerned Person is the person who prepares and arranges the documents.
-
-
-
- He/ She may be the Operator, Chemist, Officer, Executive or Head of concern department.
-
Raw Data:
- Analytical records i.e.
-
-
-
-
- Analytical reports,
-
-
-
-
-
- Original observations,
-
-
-
-
-
- Analyst hard books and
-
-
-
-
-
- All other activities carried out for the analytical purpose,
-
-
-
-
-
- Batch Manufacturing Records (BMR) and
-
-
-
-
-
- Sub-sequential logs etc.
-
-
-
-
- Note: Term “record room” is used throughout SOP for record room and / or document room.
-
Annotate:
- To add explanatory notes.
-
Document:
- A document is a physical or digital representation of a body of information designed with the capacity (and usually intent) to communicate.
-
-
-
- A document may manifest symbolic, diagrammatic or sensory-representational information.
-
-
-
- Following are some examples, but not limited to:
-
-
-
-
- 1) Standard Operating Procedures
-
-
-
-
-
- 2) Standard Test Procedures perpetual
-
-
-
-
-
- 3) Specifications
-
-
-
-
-
- 4) Master Formula
-
-
-
-
-
- 5) Manufacturing/Packaging Instructions
-
-
-
-
-
- 6) Policies
-
-
-
-
-
- 7) Analytical Data
-
-
-
-
-
- 8) Protocols/ Reports
-
-
Document Coordinator (DC):
- An individual (or a group of individuals) is responsible for coordinating and managing Documents and Records (including the secure storage, archival, retention and destruction of documents/records) within their purview in accordance with relevant procedures.
-
Product Life cycle:
- The period between a product’s development stage up through expiry of the last batch of the product commercially distributed under the Product Application with the relevant Regulatory Agency (ANDA, etc.) is called the Product Life cycle.
-
-
-
- This life cycle is inclusive of the process of technology transfer from R&D to Manufacturing Site in which the product has undergone its process optimization (feasibility and scale-up) and manufacturing of Registration batches.
-
Electronic Record:
- Any combination of text, graphics, data, audio, pictorial or other information related to cGxP activity represented in digital form that is created, modified, maintained, archived, retrieved or distributed by a computer system.
-
cGxP :
- cGxP is a general term that stands for current Good “x” Practice (x = Clinical, Engineering, Laboratory, Manufacturing, Documentation, Pharmaceutical, etc.).
-
-
-
- The titles of these Good “x” Practice guidelines usually begin with “Good” and end in “Practice”. cGxP represents the abbreviations of these titles where “x” a common symbol for a variable, represents the specific descriptor.
-
Perpetual:
- Perpetual documents are the documents for which the retention period is not possible to declare.
-
-
-
- These documents shall destroy after proper review of the history of the product and assurance that the documents are obsolete and no longer required.
-
6.0 PROCEDURE FOR DOCUMENT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM:
-
-
Document Management System :
-
-
-
-
Logbook Issuance Procedure in Document Management System:
- All respective departments shall indent the logbook as per the requirement.
-
-
-
-
- Department shall verify the received logbooks with respect to indent than send to QA for issuance purposes.
-
-
-
- QA Designee shall issue the logbook like
-
-
-
-
- SOP training,
-
-
-
-
-
- Change Control,
-
-
-
-
-
- Market Complaint,
-
-
-
-
-
- Planned Modification,
-
-
-
-
-
- Qualification Protocol Issuance and Numbering Register,
-
-
-
-
-
- Incidence and Investigation,
-
-
-
-
-
- CAPA and any other logbooks etc.
-
-
-
-
- Record the logbook issuance in “Log Book Issuance Register” as per Annexure 4.
-
-
-
- QA Designee shall allocate the logbook No. Whichever is applicable as follows;
- For Logbook Issuance. Allocate no. as QA/L/YY/XXXX
- QA Designee shall allocate the logbook No. Whichever is applicable as follows;
-
Where,
-
-
-
-
- QA : Quality Assurance
- L : Log Book
- YY : Current year
- XXXX : Stands for the Serial No. of the issued logbook.
- For file issuance, no. can allocate as QA/F/XXXX
-
-
-
Where,
-
-
-
-
- QA : Quality Assurance
- F : File
- XXXX : Stands For the Serial No. of the issued file.
-
-
-
-
-
- All logbooks have Document status labels on the Cover page of the logbook…
-
-
-
- User shall return the logbook/document to QA after verifying by the user department as well as IPQA, through “Document Submission log” .
-
-
-
- QA shall update the “logbook issuance register” as per Annexure 4 during retrieval of issued logbook/document from the user department.
-
-
-
- If the same logbook is to be continued for next month/year then it will be again reissued with a new logbook number for next month/year.
-
-
-
-
Stamp Issue Procedure in Document Management System :
- Packing material stores shall indent all the necessary stamp for QA.
-
-
-
-
- After receiving stamps from vendor PMS will submit all stamps to QA.
-
-
-
- QA shall issue stamps to all departments and maintain a stamp issuance/destruction log (Annexure-5).
-
-
-
- Various stamps shall keep under Lock and Key provision with proper labeling.
-
Storage and Retention of cGxP, Regulatory Documents & Records:
- The Document Coordinator or designee shall receive completed documents and records for retention and shall acknowledge receipt of these documents.
-
-
-
- Store all documents and records in well-secured areas (preferably in a facility equipped to protect against damage, deterioration or loss due to fire, flood, pest infestation, moisture, etc.)
-
-
-
- Control the access to these storage areas and limited to authorized personnel.
-
-
-
- The Document Coordinator shall review the stored record(s) area and evaluate the general storage conditions of records.
-
-
-
- Any questionable or deteriorated conditions that are noted shall bring to the attention of the Department Head.
-
-
-
- The Document Coordinator shall maintain and update a log (electronic or manual) for retention (which shall be a controlled document).
-
-
-
- Fill the details in the Document Retention Log listed in Annexure.
-
-
-
- Document coordinator (owner of document management system) shall record for any temporary or permanent request to withdraw a controlled document from the document storage location and include, but not be limited to:
-
-
-
-
- Document Requested By (Sign/Date)
-
-
-
-
-
- Reason for Request
-
-
-
-
-
- Document Returned By(Date)
-
-
-
-
-
- Document Received By (Sign/Date)
-
-
-
-
-
- Authorization by Department Head or designee
-
-
-
-
-
-
Retention of Document
-
- The Document Coordinator shall retain all the Documents and Records as per the minimum retention period defined as per Annexure 10.
-
-
-
-
- The Documents and Records that need to be rapidly and easily retrieved/accessed should be stored in an active storage location, for example, a document that may be requested during a regulatory inspection.
-
-
-
- The Documents and Records having reduced usage/reference requirements where removal from active storage does not impede normal business, should be moved to inactive storage. This storage location may be off-site.
-
-
-
- In case of closure of the original document storage location, the Document Coordinator shall ensure to transfer documents/records to another secure location.
-
-
-
- All electronic records that are in the scope of this GQS shall meet the above requirements for retention, logging, transfer, and retrieval.
-
-
-
- They shall be retained according to the same criteria applied to hard-copy Documents and Records, as defined in the retention period table as per Annexure 10.
-
-
-
- All such electronic records shall meet the requirements for review of the suitability, security, and stability of the storage technologies used for retention.
-
-
-
- Only current version documents, records, and logbooks shall be kept in the respective department.
-
-
-
- Master Documents shall be kept at designated cupboard of SMEs under the provision of Lock and Key with the proper label as per Annexure -1
-
-
-
- Any superseded master documents and Sequential logbook of previous months/year, documents of previous year and old documents shall be kept at Record Room as per Annexure 10.
-
-
-
-
Document coordinator shall keep
-
-
-
-
- All retrieved logbooks/documents in record room in an adequate manner with location code as per the “Document traceability template” Annexure-7 within two working days from submission.
-
-
-
- The document coordinator shall retain all the Documents and Records as per the minimum retention period defined as per Annexure 10.
-
-
-
- The location code shall be assigned by authorized QA person during the archival of documents in the record room.
-
-
-
-
The location code number for all documents shall be assigned as per below format:
-
-
-
-
-
- Location code can be allocated as DC00/RK000/SF000/FL000
-
-
Where,
-
-
-
- DC00 is represented to Document cell No.
-
-
-
-
-
- RK000 is standing for Rack No.
-
-
-
-
-
- SF000 is standing for Shelves No.
- FL000 is standing for File No.
-
-
-
-
- All the documents shall be archived with proper “Document storage Label”.as per Annexure 3.
-
-
-
- QA shall maintain and update the soft copy of the Document Traceability template (Annexure 7) for retention.
-
-
-
- All the documents should be traceable through the Soft copy of the Document Traceability template (Annexure 7) which shall be password protected.
-
-
-
- List of Authorized Personnel as per Annexure 6 shall be displayed at the entrance of the Record room. Annexure 6 shall be revised as and when required.
-
-
-
- The user department shall submit the documents, records, and logbooks to the quality assurance department through document submission Log (Annexure 9).
-
-
-
- Keep all the completed files of the document (under document management system) with proper identification label in such a manner that provides security, protection from fire, flood or other disasters, and allows them to be retrieved easily whenever necessary.
-
-
-
- Maintain the Environmental conditions of the record room in such a way that the legibility of the information contained in the document shall not get affected.
-
-
-
- QA shall review the stored record(s) area and evaluate the general storage conditions of records. Any questionable or deteriorated conditions that are noted shall be brought to the attention of the Department Head.
-
-
-
- Document coordinator shall receive completed documents, records, and logbooks for retention and shall acknowledge receipt of these documents.
-
Issuance and retrieval procedure under Document Management System:
- Whenever if require any archived or new document/record from record room/documentation cell should be issued through “Document/Record issuance and retrieval form”. Incase of BMR/BPR.
-
-
-
- QA person shall maintain the Document Traceability template, Annexure 7.with respect to “Document/Record issuance and retrieval form”.
-
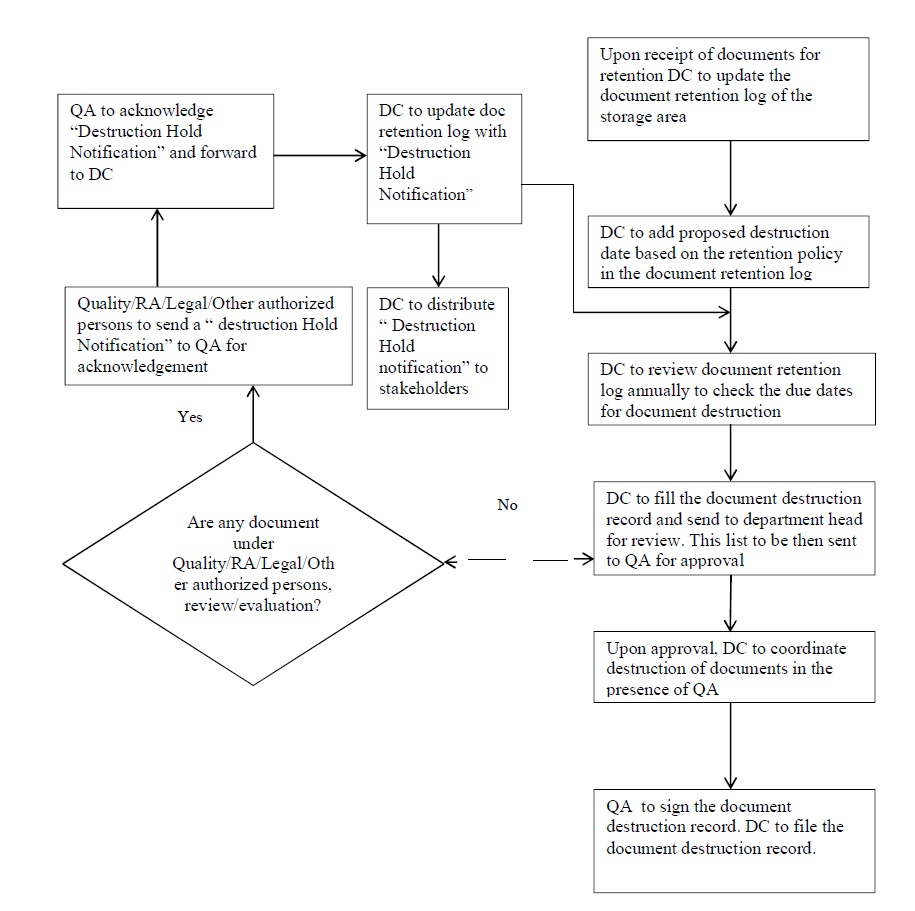
Destruction of cGXPand Regulatory Documents & Records under Document Management System:
- Destroy the Documents and Records after the end of their retention period.
-
-
-
- Prepare a list of document needs/eligible for destruction on an annual basis.
-
-
-
- However, in case such Documents and Records are associated with products that are under current Quality, Legal or Regulatory Evaluations/Review, their destruction shall be put on Document Hold until completion of evaluation/review.
-
-
-
- RA department / Legal department / Other Authorized Persons shall send a notification for hold of the destruction of such documents to QA. As per annexure-12 (Notification of Destruction Hold of Document/Record)
-
-
-
- QA shall record all such notifications related to the suspension of destruction in the Document Traceability template, Annexure 7 and shall archive all supporting documents for the same.
-
-
-
- An acknowledgment of the receipt of all such notifications shall be signed by the QA and sent to the notification sender.
-
-
-
- After getting approval for destruction from QA head, document to be destroyed by manually or with the help of paper shredding machine as per SOP.
-
-
-
- In the case of electronic documents/ records, the destruction of data may be completed by means of erasure/deletion from the storage medium by QA.
-
-
-
- Maintain the destruction record after destroying the document as per Annexure 11.
-
-
-
-
QA shall file all destruction records.
-
-
-
-
- The Document Coordinator shall review and make a list of documents on an annual basis.
-
-
-
- The Document Coordinator shall prepare a document destruction record (example template provided as per Annexure 11 listing such documents and submit the destruction record to their Department Head for verification.
-
-
-
- The Department Head/Designee shall verify that the documents/records listed for destruction are eligible to be destroyed based on the approved retention procedures and document hold notifications.
-
-
-
- After verification by the Department Head/Designee, the Document Coordinator shall send the document destruction list to QA and/or Identified Responsible Person for approval of the planned destruction.
-
-
-
- After receipt of document destruction approval from QA and/or Identified Responsible Person, the documents/records shall be incinerated/ shredded in the presence of QA / Identified Responsible Person in a manner that renders them completely illegible/unusable.
-
-
-
- In the case of electronic documents/records, the destruction of data may be completed by means of erasure/deletion from the storage medium by a responsible person so as to render them unrecoverable and unusable.
-
-
-
- Take the signature QA/identified Responsible Person for the document destruction records as a verification of the destruction process.
-
-
-
-
The Document Coordinator shall file all document destruction records.
-
-
-
-
- In case a product/equipment/instrument is transferred to another site, the original documents/records of such a product/equipment/instrument shall be transferred along with it.
-
-
-
- Retain a photocopy of the same at the site as per the defined retention procedures.
-
-
-
- Any cGxP documents or records not specifically addressed in the List of Retention Period (Annexure-10) below shall be retained for a minimum of 1 year after its use until the finalization of a retention period for the same.
-
-
-
- Brought to the attention of the Quality Head for determination of the Responsible Person(s) most qualified to establish the retention times such that it can be included in the next revision of the Retention Period Table.
-
-
-
- In case of a document/record is lost or destroyed before the destruction date defined in the Retention Schedule. Raise the incident for the same.
-
-
-
-
In the case where cGxP documents are made obsolete, the obsolete Master Copy of the last version shall be retained up to the end of the facility/product lifecycle (as applicable).
-
-
-
-
- The specified retention period is applicable to all types of documents/reports irrespective of the format i.e. hard copies or electronic records or those in other enterprise software systems like SAP, etc.
-
-
-
- Photocopy the thermal printing documents and Retain with the photocopy for the period specified as per Annexure 10- Retention Periods of GCP Documents / Records.
-
-
-
- Retain the documents in the enterprise systems such as SAP for a minimum retention period specified as per Annexure 10 – Retention Periods of GCP Documents/Records.
-
-
-
- However, the responsible departments may consider retaining these a longer period than the specified retention period based on their relevant SOPs.
-
-
-
- Store the records under secure controls to prevent loss or damage, e.g. fire, water, with access restricted to authorized personnel.
-
-
-
- Storage conditions shall minimize the risk of inadvertent destruction or alteration, deterioration and/or damage.
-
-
-
- Maintain the GMP record lifecycle in controlled areas by assigned personnel to ensure
-
-
-
-
- Classification,
-
-
-
-
-
- Versioning,
-
-
-
-
-
- Traceability,
-
-
-
-
-
- Storage,
-
-
-
-
-
- Authenticity,
-
-
-
-
-
- Retrievability and
-
-
-
-
-
- Security of the records stored within them.
-
-
-
-
- Retrieve the Records promptly and readable in either hardcopy or electronic form over their full retention period for purposes including audits, inspections, and disposition.
-
-
-
- Include the GMP Documents and Records in and appropriately protected as part of the Crisis Management and Disaster Recovery Plan.
-
7.0 DISTRIBUTION of SOP for Document Management System:
-
- Environment, Health, and Safety
-
- Information Technology
-
- Maintenance
-
- Personnel and Administration
-
- Production
-
- Quality Assurance
-
- Quality Control
-
- Warehouse
Refer to Article: Document Retention Period in Pharmaceuticals for more details about document retention. – Click here…
Flow Cart for Document and Record
Click to download Annexures: Document Management System



Pingback: SOP for Drug Product Recall & Mock Recall - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Site Master File (SMF) Preparation SOP & Guideline - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Good Documentation Practices - SOP & Guideline - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: GxP Record Retention and Archival Policy in Pharma - Pharma Beginners