The manufacturer or supplier who is supplying the material in routine and registered for the supply of specific material after the approval process considered as an approved vendor. Vendor management consists of the Identification, Qualification, Requalification, management of changes at the vendor site, Vendor Audit, Technical Agreement, Deregistration Process, etc.
Vendor Management
1.0 PURPOSE:
-
- The objective of this Standard operating procedure (SOP) is to describe a standard for the management of Vendors to get consistent quality of Raw Materials, Primary, and Printed Packaging Materials.
-
-
-
This SOP comprises the concepts of:
-
-
-
-
- Qualification of New Vendors
-
-
-
- Qualification of Existing Vendor for New Material
- Qualification of Existing Vendor for New Material
-
-
-
- Requalification of Vendors
-
-
-
- Management of changes related to Vendor
-
-
-
- Vendor Audit
-
-
-
- Technical Agreement
-
-
-
- De-registration Process
-
-
-
- Evaluation of Supply for Quality (Q Score)
-
-
-
- Annual Risk Assessment
-
2.0 SCOPE:
-
- This SOP is applicable to Management of Vendors of the following materials:
-
-
- Raw Materials (API and Excipients) used in Drug Product Manufacturing.
-
-
-
- Product-contact Packaging Materials (Primary Packaging Material).
-
-
-
- Printed Packaging Materials, Packaging Material with other kinds of identification e.g. imprint or embossing.
-
3.0 RESPONSIBILITY:
-
-
Head commercial department or designee shall be responsible for
- Identifying the Vendors and generate Vendor Code.
-
-
- Arranging for duly signed Technical Documents from the Vendor.
-
- Arranging samples for Quality evaluation (as applicable).
-
- Coordinating for Vendor’s Manufacturing Site Audit and response.
-
- Ensuring appropriate and timely actions for Vendor(s) categorized“Under Observation”.
-
- Coordinating with Vendor for response and corrective/ preventive actions for reported nonconformity.
-
- Coordinating with Vendors as and when needed on the subject to arrange to meet.
-
- Intimating for Warning Letter / Import Alert information received from Vendor to Vendor Qualification Office.
-
- Supporting Vendor De-Registration process.
-
Head vendor qualification office or designee shall be responsible for
- Ensuring the availability of valid vendor technical documents at manufacturing locations/sites, R&D sites, and FDD (Formulation Development Department) through Commercial.
-
- Reviewing and Approval of vendor technical documents for adequacy and update the status in the Electronic / Manual System as applicable.
-
-
Maintaining and update Centralized Vendor Document Data bank with respect to but not limited to:
-
-
-
- Vendor Information Form (VIF)
-
-
-
- TSE BSE Certificate
-
-
-
- Residual Solvent Certificate
-
-
-
- Audit Report
-
-
-
- Compliance Report
-
-
-
- Audit Closure
-
-
-
- Technical Agreement
-
-
-
- De-registration of Vendors (as applicable)
-
-
- Sharing the audit report of vendor categorized as “Under Observation” with concern QA Head to support Risk Assessment at the site.
-
- Communicating details of the vendor De-registration to respective Site Quality and Commercial.
-
- Reviewing the status of “Under Observation” vendor(s) bi-monthly in coordination with Commercial.
-
- Submitting Monthly Report to Head Corporate Quality Audit.
-
- Supporting resolution of queries/deficiencies reported by Regulatory Authorities / Customer Audits (as applicable) for the vendor management process.
-
- Managing of Warning Letter / Import Alert of Vendor.
-
-
- Coordinating “For Cause audits”.
-
-
-
- Reviewing Annual Risk Assessment from Sites and prepare the yearly Audit Planner.
-
-
-
- Reviewing the list of Qualified Auditors.
-
-
-
Corporate quality audit regional head or designee shall be responsible for
- Coordinating with the Commercial Department for Vendor’s Manufacturing Site Audit.
-
-
- Conducting Vendor Site Audit and Qualify the Vendor as “Approved”, “Not Approved” or “Under Observation”.
-
- Ensuring the preparation, approval, and authorization for distribution of vendor audit reports and forward to Commercial.
-
- Ensuring compliance from Vendor through Commercial and verify the adequacy.
-
- Responsible for ensuring that audit, compliance reports, and audit closure are submitted to the Vendor Qualification Office as per the respective timelines as per this SOP.
-
- Raising vendor de-registration proposal as applicable.
-
- Tracking and Monitoring of Audit Planner.
-
- Authorizing the audit report in case the vendor is categorized as“Under Observation” or “Not Approved”.
-
- Approving Vendor De-registration Proposal.
-
- Approving Audit Closure.
-
- Ensuring training, certification, and enhancement of audit skills of auditor(s).
-
- Allocating need base resources for the Audit Program.
-
- Supporting Management Review Process.
-
- Approving on conclusion note (Import Alert / Warning Letter)
-
Head Quality or designee shall be responsible for
- Ensuring the availability of vendor technical documents through electronic/ Manual System.
-
- Ensuring approval of vendor as per current site Standard Operating Procedure.
-
- Updating the Vendor status in an electronic or manual system whichever is applicable.
-
- Performing Risk Assessment for the vendor categorized as “Under Observation”.
-
- Maintaining Approved Vendor List and its distribution to concerned departments.
-
- Raising vendor de-registration proposal (need base).
-
- Sharing product specific requirement with the vendor through commercial as applicable.
-
- Performing the Annual Risk Assessment.
-
- Approve the Risk Assessment for Handling Regulatory Restrictions as appropriate.
-
Head regulatory affairs or designee shall be responsible for
- Notifying Vendor Qualification Office for any Warning Letter / Import Alert Information.
-
Head corporate IT or designee shall be responsible for
-
- Supporting electronic system operations.
-
- Updating Supplier Master as applicable.
-
- Supporting in the De-registration process.
4.0 PROCEDURE OF VENDOR MANAGEMENT:
-
- It is a total quality management system that assures that materials procured from Vendors are manufactured, packaged, and shipped under a controlled process that results in consistent conformance to quality as per company quality system.
-
- Vendor management shall consider based on a specific component, the active ingredient, container, or closure type.
-
- Qualification/deregistration of the vendor shall be specific for the site of manufacture of Vendor/material and not for the Vendor’s company as a whole.
-
- The vendor may be the Manufacturer and/or Supplier, providing material from the aspecific site.
-
- All deviations in the process of vendor management as per site-specific SOP shall mandatorily be approved by QA Head.
-
- The commercial department shall coordinate for potential Vendors from available resources and the Vendor management process shall be as described in this standard.
-
- Manufacturers of API, KRM, Key Excipients and Primary, and PrintedPackaging Materials will be subjected to audits based on the outcome of the annual risk assessment or defined frequency which is earlier.
-
- In general re-qualification of Manufacturers of API shall be carried out once in three years.
-
- For Key Excipients, Key Raw Materials, and Primary and Printed PackagingMaterials re-qualification of Manufacturers shall be carried out once in five years.
-
Qualification of new vendors under vendor management:
- Vendors shall be identified by Commercial in consultation with other departments such as
-
-
- Product Technology Development(PTD),
-
-
-
- Process Technology Transfer (PTT),
-
-
-
- Chemical Research Division (CRD),
-
-
-
- Product Development Research (PDR), etc., as applicable.
-
-
- The identification of a new Vendor shall be based on the assessment of the Vendor’s capability to supply the material with consistent quality standards set by the company.
-
- All new Vendors shall be verified whether they are Manufacturers Suppliers for a particular material.
-
-
The following rules shall apply for Vendor qualification /vendor management:
-
-
- When the Vendor is the Manufacturer and the Supplier, the Vendor shall be qualified as a single entity.
-
- When the Vendor is a Supplier who is not a manufacturer and does not carry out any ’partial manufacturing’ activity,
-
- Only the Manufacturer needs to be qualified by the company for all the applicable criteria based on the type of material procured.
-
- The Vendor is a Supplier who is not a manufacturer but carries out a ‘partial manufacturing’ activity, Vendor Qualification will need to be carried out for both Supplier and Manufacturer.
-
- In case of a change of manufacturing site by the Vendor, the qualification process shall be repeated.
-
- In the case where, there is a change in manufacturer names because of merger or acquisition, and no change in quality, manufacturing site, and service of products, the qualification process is not required to be repeated,
-
- However, a declaration from the Vendor shall be mandatory and a change in Vendor / Manufacturer name shall be intimated by Vendor Qualification Office to respective manufacturing sites through the electronic or manual system as applicable.
-
-
Upon identification of a new Vendor, the following documents shall be requested by a commercial from the Vendor as a prerequisite:
- Vendor Information Form (VIF) stating whether the vendor is Manufacturer / Supplier / Manufacturer andSupplier.
-
-
- This form shall be submitted by all active vendors, in case any changes occur at a later date, the same shall be communicated by the Vendor through a revised VIF for vendor management.
-
- If the identified Vendor has a format for the self-assessment questionnaire, which meets company expectations,
-
- The same can be used in lieu of the company Vendor Information Form.
-
- TSE/BSE Risk Evaluation Questionnaire to be filled by the Vendor if the material under consideration is prepared from animal origin.
-
- If the material is not from animal origin, a declaration from the Vendor regarding TSE/BSE risk-free material must be taken stating that the material is not produced from animal sources and
-
- No material of animal origin is used in the manufacturing process of the same under vendor management.
-
- If this assessment has already been done by any regulatory authority and certification is available (e.g. TSE certification by EDQM), a copy of this certification may be used in lieu of a questionnaire for TSE/BSE risk evaluation.
-
- Vendor Qualification Office designee shall ensure the vendor mandate technical documents for its suitability, adequacy, and completeness as per the respective procedure.
-
- Maintain the centralized vendor document database, vendor-site wise-molecule-wise through the electronic or manual system by Vendor Qualification Office designee.
-
Vendor Document Validity :
Table A: Documents Validity
| Name of Document | Existing Valid Till | Initiate Process for the revised document |
| VIF, TSE BSE Certificate, Residual Solvent, Declaration and Other Technical Documents as per Table B | API: 4 Years from date of Review and approval. KRM/KE/Primary and Printed PM: 6 years from the date of review and approval. |
API: 3 Years
KRM/KE/Primary and Printed PM: 5 years |
| Audit Report and Technical Agreement | API: 4 Years from date of the audit
KRM/KE/Primary and Printed PM: 6 years from the date of audit. |
NA |
-
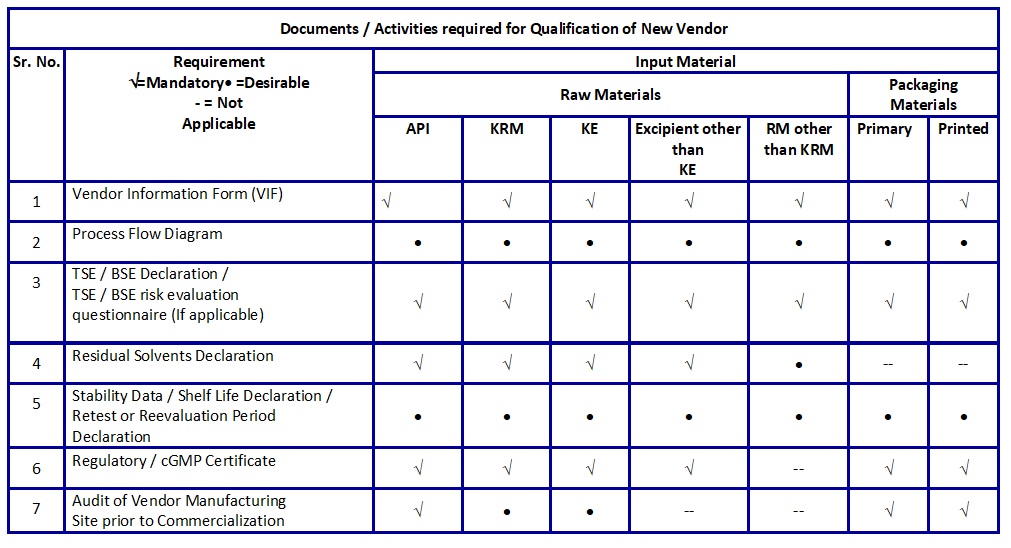
- Vendor Technical documents required for the qualification of a new vendor are listed in Table B.Retention of Vendor Document / Reports.
-
- The hard copies of vendor technical documents, audit reports, and compliance reports along with evidence (as available) shall be retained for a period of 06 years or one revision whichever is earlier.
Table B: Documents / Activities required for Qualification of New Vendor
-
- Notes: Any other document necessary for Vendor Qualification, such as
-
-
- Food Grade Certificate,
-
-
-
- Melamine Free Certificate,
-
-
-
- Genotoxic Impurity Evaluation Report,
-
-
-
- Analytical Method Validation Reports,
-
-
-
- Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR) Certificate,
-
-
-
- Benzophenone Declaration etc. may be requested on case to case basis.
-
-
- Materials procured from Internal Sites/ Affiliates, vendor qualification mandate documents based on the type of material under procurement shall be required as a part of the Vendor Qualification Process.
-
- In all such cases, the Technical Agreement is required for Internal Sites under vendor management.
-
- In case material procured from Third Party or Loan License manufacturing units, all qualification documents as per Table B and copy of the Technical Agreement between the company and Third Party or Loan License Manufacturing Sites shall be obtained.
-
-
Commercial shall arrange for samples along with Vendor’s COA for testing and evaluation at site QC / Analytical Research (AR) Laboratories.
-
-
- Additionally, qualified/validated method(s) of analysis, impurities, working standards, etc., as applicable and if needed, shall be arranged.
-
- However, in case of materials that are hazardous in nature i.e. solvents and gases, they may be evaluated based on the review of the Vendor’s COA vis-à-vis desired company specification along with the TSE/BSE Certificate received from the vendor.
-
- Samples shall be analyzed by QC / AR or any other Qualified Laboratory as per In-house or Vendor’s method.
-
- Materials procured from the Vendor for evaluation shall meet the desired specification (under vendor management).
-
- The samples should be from the same manufacturing site and the same manufacturing process.
-
- The minimum number of samples required for testing and evaluation shall be as per the following table (Table C):
Table C: Samples requirement for testing and evaluation
|
Material Type |
Number of Samples required |
| API, Excipients & KRM for API manufacturing | Minimum Three different batches/lots (preferably consecutive) |
| Raw Materials other than KRM for API Manufacturing, Primary Packaging Material | Minimum Three different batches/lots (preferably consecutive) |
| Packaging Material other than Primary Packaging Material, Hazardous Material, Solvents, Gases, Material manufactured and tested by any other Manufacturing Site | Not required |
-
- Based on satisfactory data of complete analysis, R&D Development Batch data, and Site Exhibit Batch data, material from Provisionally Approved Vendor can be used for Process Validation.
-
- However, QA head to ensure the availability of audit reports prior to commercialization.
-
- Based on satisfactory data of complete analysis and R&D Development Batch data, Material from the new vendors can be used for Exhibit Batch.
-
- In case of a significant difference between Manufacturing Site results and the Vendor’s COA, an investigation shall be done to find out the root cause and appropriate corrective action shall be taken.
-
- Corrective action shall depend on the finding of investigations. Upon satisfactory investigation and corrective action, if needed, the Vendor may be asked to provide a fresh sample for evaluation.
-
-
The same test method(s) shall be used at Manufacturing Sites and Vendor end.
-
-
- Test method(s) may be shared with the Vendor and mutually agreed by both the parties under a confidentiality agreement if needed.
-
- Any subsequent changes in such test method(s) shall be shared with the Vendor.
-
- The company may also decide to use methods developed and validated by the Vendor or monograph methods (in case of excipients).
-
- In the case of API, KRM, KE, and Primary Packaging materials, if the sample complies as per the specification, trials for a feasibility study of the material may be taken by Product / Packaging / Process Development Laboratories, if warranted.
-
- Products from batches used for material feasibility study trials should meet desired specifications for release. Such products also are placed understandability studies if needed as per Site-specific SOPs/ current regulatory guidance.
-
- In order to establish the consistency of product within the container and among the containers as a prerequisite of vendor approval following the sampling plan shall be followed by Site Quality for minimum first two consignments:
Sampling Plan for Drug Substances (APIs):
| Sample Quantity | Sampling Pattern | Tests* |
| If less than or equal to 5 kg quantity available in one container. | A composite sample from all the three layers. | Complete analysis as
per specification. |
| From the individual container, samples from the top layer, and composite sample. | Loss on Drying/ Water Content and Description Tests. | |
| From the individual container, samples from the middle layer, and composite sample. | Loss on Drying/ Water Content and Description Tests | |
| From the individual container, samples from the bottom layer, and composite sample | Loss on Drying/ Water Content and Description Tests. | |
| If no. of containers is greater than 10, then divide no. of containers by 3.
For Example, For 71 containers (e.g. 71 containers/ 3 = 24), pool one contains 1 to 10, the second pool of containers 11 to 20, and the third pool of containers 21 to 24. Composite sample preparation shall not be exceeded by more than 10 numbers. |
1st set of containers (No. 1 to 10) samples from the top layer, and composite sample. | Description, Loss on drying/ Water content tests. |
| 2nd set of containers (No. 11 to 20) samples from the middle layer, and a composite sample | Description, Loss on drying/ Water content tests. | |
| 3rd set of containers (No. 21 to 24) samples from the bottom layer and a composite sample | Description, Loss on drying/ Water content tests. | |
| Prepare a composite sample from all three layers individually for different sets mentioned above. | Complete testing as per the specification | |
| Separate QC testing sample provided by the vendor, due to the highly hygroscopic and sensitive nature of the material. | As per specific SOP | As per specific SOP |
Note:
For all consignments, regardless of the number of containers, the Identification test shall be performed on each container. “*” – Testing should be performed considering the criticality of parameter and as per specification.
Sampling plan for excipients:
| Sample Quantity | Sampling Pattern | Tests* |
| If less than or equal to 5 kg quantity available in one container. | A composite sample from all the three layers. | Complete analysis as per specification. |
| If √n + 1 = Less than or equal to 10 no. of containers | Containers to be sampled from Top Layer & Composite Sample. | Description, LOD & Water Content Tests. |
| Containers to be sampled from Middle Layer & Composite Sample. | Description, LOD, and Water Content Tests. | |
| Containers to be sampled from Bottom Layer & Composite Sample. | Description, LOD, and Water Content Tests. | |
| Composite Sample of all the above samples | Complete Analysis as per specification | |
| If. √n + 1 = Greater than 10 no. of containers then divide no. of containers by 3 and then, (e.g. 200 containers, √n + 1 = 15 then 15/3 = 5 containers) | From the 1st set of containers (5 containers) samples from the top layer, and a composite sample | Description, Loss on Drying/ Water Content Tests. |
| From the 2nd set of containers (5 containers) samples from collected middle layer and composite sample. | Description, Loss on Drying/ Water Content Tests. | |
| From the 3rd set of containers (5 containers) sample from the bottom layer & composite sample. | Description, Loss on Drying/ Water Content Tests. | |
| Prepare a composite sample from each layer (Top/Bottom & Middle). | Complete Analysis as per specification | |
| Separate QC testing sample provided by the vendor, due to the highly hygroscopic and sensitive nature of the material. | As per Specific SOP | As per Specific SOP |
-
Note:
- For all consignments, regardless of the number of containers, the Identification test shall be performed on each container. “*” – Testing should be performed considering the criticality of parameter and as per specification.
-
- For further commercial consignment received, QC shall analyze the samples as per the site SOP on “Testing and Releasing of Raw Materials”.
-
- Vendor Audit shall be performed after all the documents have been reviewed, sample evaluation completed, and performance trials if any are satisfactorily completed but prior to commercialization of the product.
-
-
Conclusively, approval of New Vendors shall be based on the following (but not limited to):
-
-
- Review of vendor qualification mandate documents as listed in Table B.
-
- Review of sample evaluation results to review specification compliance and feasibility study in the case warranted by R&D / PTD.
-
- Based on review and assessment, Site Quality shall update the respective vendor status as per their Site-specific SOP in the electronic or manual system as applicable.
-
Approved Vendor(s) List:
- The Approved Vendor list shall be maintained electronically/ manually by Site Quality.
-
- Electronically generated Approved Vendor lists shall have the following details:
-
- Printed By (User ID)
-
- Date of Print (System ID)
-
- The approved Manufacturer(s) list shall contain (but not limited to): Material Description, Material Code, Manufacturer’s Name, Manufacturer’s Code, Address of Manufacturing Site, and Validity of Approval.
-
- In the case of a manual list, the site shall review annually at the beginning of the calendar year for any updates.
-
- Site Quality is responsible to maintain the list and revision or version number of the Approved Vendor List.
-
- Attache a duly approved addendum to the list in case new vendors are approved during the year.
-
Numbering System of Approved Vendor List:
- QA shall assign the approved vendor list number as per the below-mentioned procedure.
-
- The approved vendor list number shall be i.e. AVL/XXX/YY.
-
- AVL stands for the approved vendor list.
-
- XXX stands for item identification like API, PKM, and EXP. This code represents the item code as follows:
-
- API: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient
-
- PKM: Packing Material
-
- EXP: Excipient
-
- YY: Represents the version number of the approved vendor list.
-
Qualification of existing vendor(s) for new material(s):
- Procedures, as described above, shall be followed suitably for Qualification of Existing Vendor(s) for a NewMaterial(s).
-
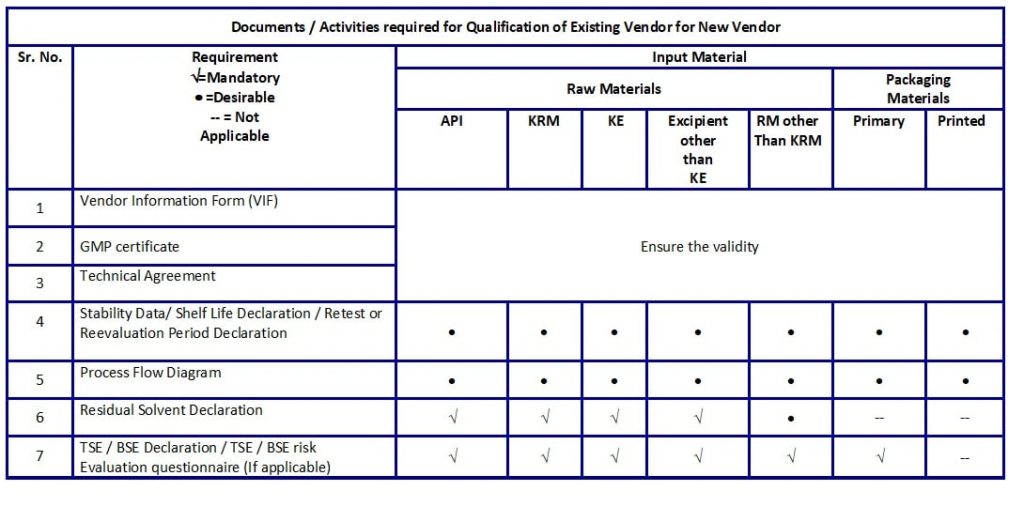
- Documentation requirements for Qualification of Existing Vendor(s) for New Material(s) are as mentioned in Table D.
Table D: Documents / Activities required for Qualification of Existing Vendor for New Vendor
-
-
Re-Qualification of the existing vendor(s):
- Any other document necessary for Vendor Qualification, Such As
-
-
-
- Food Grade Certificate,
-
-
-
- Melamine Free Certificate,
-
-
-
- Genotoxic Impurity Evaluation Report,
-
-
-
- Analytical Method Validation Reports,
-
-
-
- Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR) Certificate,
-
-
-
- Benzophenone Declaration etc. may be requested on case to case basis.
-
-
- Documents required for the Re-qualification of Vendors shall be as per the mandatory documents defined in Table B.
-
- Audit requirement of the manufacturing site of Vendor during the Requalification of existing Vendors for API, KRM, KE, PrimaryPackaging Materials, and Printed Packaging Materials shall be based on the Annual Risk Assessment provided by the Manufacturing Site.
-
- However, preferably for API audit of the vendor shall be conducted once in three years and for KRM/ KE/PrimaryPackaging Materials and Printed Packaging Materials once in five years irrespective of Annual Risk Assessment.
-
- Vendor Documents will remain valid as per the validity provided in Table A.
-
Management of changes related to the vendor – Vendor Management
- Management of changes related to the vendor shall be governed by the site quality system and SOP of Change Control Management.
-
Vendor Audit Management:
- Audit of Vendors of API, Primary Packaging Materials, and PrintedPackaging Materials shall be preferably done before taking up exhibit batches. But mandatorily before Commercial batches are manufactured using the Vendor’s material.
-
- Vendor Qualification Office shall update the onsite audit request for new vendors based on information forwarded by Site Quality, SiteR&D, or any other source.
-
- Vendor Qualification Office shall prepare the annual audit planner based on the Annual Risk Assessment received from the Sites, Audit Request Forms, and request from Regulatory Affairs and on the basis of requalification criteria for audit.
-
- The Quarterly Audit schedule shall be prepared by the Vendor Qualification Office based on the confirmation of audit data received from the vendor through commercial.
-
- For Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API) the audits shall be conducted at the frequency of three years from the last audit date.
-
- For Primary Packaging Materials and Printed packaging materials, KRM and KE audit shall be conducted at the frequency of five years from the last audit date. However, a need-based audit can be triggered while introducing a new molecule.
-
- Auditors preferably accompanied by a Commercial representative shall perform vendor’s quality systems audit. In the case of For Cause Audit, Site Representative shall conduct and/or accompany the lead auditor need-based.
-
- The focus of the audit shall be the assessment of the Vendor’s cGMP compliance level as per relevant Regulatory Guidelines like ICHQ7, EU GMP, and ISO 15378 Guideline, etc.
-
-
The auditor shall verify whether proper policies/procedures/process controls exist and are followed to assure the product’s SISPQ requirements.
-
-
- During the audit, ensure the vendor’s capabilities for manufacturing, technical competency, and GMP systems. Based on the severity of audit findings, the vendor shall be categorized as “Approved”, “Not Approved” or “Under Observation”.
-
- The audit report shall be prepared and forwarded to the commercial for distribution to the vendor within 30 calendar days.
-
- Audit Report for API/KRM/KE/Primary Packaging Materials and Printed Packaging Materials shall be prepared covering applicable clauses of CGMP guidelines and can be modified as a need base.
-
- Commercial to arrange for the response against the audit observation within 30 calendar days.
-
- On a satisfactory review of the response, audit closure shall be issued for the respective vendor.
-
- In the case of vendor categorized as “Under Observation” based on the audit, the audit report shall be shared with the Site for risk assessment and mitigation plan as per Site-specific SOP.
-
- Commercial shall review the status every month and further actions shall be executed to change the status of the vendor as approved or deregistration in the time frame, not more than 6 months.
-
- Vendor Qualification Office designee shall maintain records for Audit and Compliance reports Vendor wise / Site wise / Date wise.
-
-
The current audit report and compliance report shall be considered as valid as per the timeline provided in Table A.
-
-
- Vendor Qualification office is responsible for ensuring necessary action, for the vendors to whom warning letter/ Import alert/discontinuation of CEP or country-specific regulatory restriction for the supply of material.
-
- In case of critical rejections related to material supplied by a vendor in one of the company Sites, Corporate Quality shall ensure all other Impacted Sites are notified for necessary actions.
-
-
Need base audit can be handled through the Group Audit/ Third Party Audit.
-
-
- The audit report can be purchased from the third party after evaluating the adequacy of trained and qualified staff having knowledge of cGMP regulations for conducting the audit.
-
- In the case of Vendors already existing in subsidiary companies, their Audit Reports may be accepted by the company/location based on the ExistingAgreement / CDA between the company & affiliates.
-
- Vendors may be qualified on the basis of the Paper Audit.
-
- This may include evaluation of Vendor Technical Mandate or equivalent document, copy of cGMP (Current Good Manufacturing Practices)certificates issued by competent Regulatory Authority or Certification Agencies like ISO, etc. under one or more of the following circumstances:
-
-
- Patent related issues.
-
-
-
- Vendor’s company policy to restrict audit.
-
-
-
- Confidentiality related issues.
-
-
-
- Active substances are not true APIs.
-
-
- However, in such cases, there should be clear specifications for the material being procured and this specification shall be agreed upon with the manufacturer.
-
- Regulatory requirements of a market where the product is going to be supplied shall also be considered by the corporate Quality Audit for Audit Waiver.
-
Auditor Qualifications under Vendor Management :
- Educational Qualifications: An Auditor shall have a minimum Bachelor’s Degree in the relevant Scientific /Technical Field.
-
- Experience:
-
- An Auditor shall have a minimum of 5 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry (API or Drug Product) in the Quality Management Function with at least 2 years in the Quality Assurance role.
-
- The auditor shall have specific knowledge and experience of the requirements of cGMP and must have participated in at least three GxP (as applicable) audits as Co-auditor.
-
- Certification as a “Qualified Auditor” from an External Agency is preferable.
-
- List of Qualified Auditors shall be reviewed for any addition or deletion of information once in a year or as and when required.
-
- The detailed curriculum vitae (CV) which cover the Educational, Experience & Training related information shall be maintained & archived at Corporate QualityAudit Office along with Job Description (JD).
-
- Qualified Auditor shall follow the Corporate Code of Conduct for audit.
-
The Technical Agreement under Vendor Management:
- Technical Agreements shall be obtained from Vendors of APIs, Excipient, KRM, Primary Packaging Materials, and Printed Packaging Materials.
-
- The agreement shall be printed on the company’s official Letter Head.
-
- Technical Agreement shall be entered with Vendors for API, KRM, KE, and Primary Packaging Materials and Printed PackagingMaterials to ensure commitment for adhering to the applicable guidelines.
-
- Changes in contents of the Technical Agreement shall be done with mutual consent between the company & Vendor and acceptable on Vendors Letter Head.
-
- Technical Agreement shall be signed with the Vendor after successful completion of the Audit for API and Primary Packaging Materials and Printed Packaging Materials as applicable.
-
- Technical Agreement shall be obtained from Vendor for KRM andKE prior to commercial procurement.
-
- The agreement shall be required if the material is manufactured and supplied by a company manufacturing site to another site.
-
- Amendments related to products from an Approved Vendor may be incorporated in the Existing Technical Agreement with the Vendor by the Vendor Qualification Office.
-
- Review and Approval of Technical Agreement with the Vendor shall be preferably managed centrally by Vendor QualificationOffice.
-
- The validity of the Technical Agreement is as mentioned in Table A and/or major change like manufacturing site change, senior management change whichever is earlier.
-
Handling the consignment(s) from a new vendor at the plant (Vendor Management):
- On receiving of consignment from a new vendor, the warehouse shall check the vendor details against the approved vendor list.
-
- If it is not available then the intimate Quality assurance department for Evaluation of Vendor and Metis entry after evaluation data share with FDD.
-
- In the case of the manual list (For Vendor List), the site shall review annually at the beginning of the calendar year for any updates.
-
- Site Quality is responsible to maintain the list and revision or version number of the Approved Vendor List. A duly approved addendum may be attached to the list in case new vendors are approved during the year.
-
- The warehouse shall receive the consignment after QA Approval and shall prepare the good inward memo (GIM).
-
- QC shall collect samples as per prevailing SOP on “Raw material sampling”.
-
- While sampling, quality control/Warehouse shall check the integrity of containers, manufacturers’ seal, and correspondence between the delivery note and the label. QC shall ensure that results are within the specification.
-
- On receipt of the result of the analysis, QA shall comply with all documents. On finding satisfactory, QA shall issue an updated version of the “Approved Vendor List” and retrieve the earlier version.
-
Handling rejected consignment from the approved vendor (Vendor Management) :
- In the case of rejected consignment from the approved vendor, Head quality shall send a “rejection note” to the commercial department and to Corporate Compliance.
-
- The commercial department shall inform the vendor regarding the rejection of consignment.
-
- In the case of two consecutive rejections of consignments, the vendor shall be kept under observation.
-
- Head Quality shall evaluate the results and decide on the further course of action.
-
- If require, Head Quality shall intimate Corporate Compliance to schedule for vendor’s site audit, to evaluate the vendor’s understanding of the GMP requirements, Quality assurance systems, and manufacturing condition and control on the process.
-
- Corporate Compliance shall issue an audit report to the vendor and shall get a compliance report, through the commercial department.
-
- On satisfactory compliance, Corporate Compliance shall intimate plant Quality Head regarding the outcome of the audit. At Plant, QC shall continue the evaluation of consignment(s) till three approved consignments are received.
-
Discontinuation / Deregistration of approved/new vendor (Vendor Management):
- Head Vendor Qualification Office, Quality, HeadCommercial or Designee, may raise the “Vendor Deregistration Proposal”.
-
- Criteria (but not limited to) for Deregistration of Vendor:
-
-
- Critical
-
-
-
- Annual Risk Assessment Data
-
-
-
- Critical Non-conformance observed during Surveillance audits. (Critical Non-conformance: which directly/indirectly affects the Quality, Safety, Purity product and which are not complying with cGMP Practices).
-
-
-
- If the Vendor is suspended by the respective Regulatory Authority.
-
-
-
- In case the item code is made “Obsolete” by the company.
-
-
-
- Material is not procured from the Vendor for the minimum “Three Years”.
-
-
-
- Vendor violets the Commercial Agreement/on termination of Commercial Agreement.
-
-
-
- The vendor stops the manufacturing of the product/change in the Name of the Vendor/change in the Manufacturing Site.
-
-
-
- Denial for audit by Vendor without justified reason.
-
-
- The vendor shall be deregistered for specific to material/materials, specific site, or block within one site depending upon the reason for deregistration.
-
- The de-registration status of the vendor shall be communicated to Site Quality by Vendor Qualification Office.
-
Continuous evaluation of supply for quality (Q score):
- The performance of all vendors for quality shall be evaluated by calculation of their Q Score.
-
- The Q Score calculation shall be done electronically or manually with the following logic for every:
-
-
- Approved batch/lot, the vendor shall get 100points.
-
-
-
- Rejected batch/lot (on quality parameters), the vendor shall get 1 point.
-
-
-
- Partly accepted / partly rejected batch/lot, the vendor shall get 50 points.
-
-
- In case of any on-line rejection where the reason for rejection is confirmed as a problem with material supplied by the vendor e.g. presence of foreign matter,non-homogeneity of material, presence of suspended matters in case of liquid material, etc. and not due to reasons attributable to storage conditions at different Sites, the vendor shall get 10 points or 60 points depending upon total rejection of part rejection respectively.
-
-
The overall Q Score is calculated by the formula:
-
Total earned score/number of the batches (or lots)
-
- A vendor with a ‘Q Score rating’ of more than 90 % shall be continued as an approved vendor.
-
- For vendors with Q Score less than 90%, QA shall conduct an evaluation by considering past supply history, the number of batches supplied, the reason for rejections, interaction with the vendor, etc.
-
- Based on the outcome of the evaluation, Site Quality shall justify whether to continue with the procurement of material from the vendor or not.
-
Annual risk assessment (Vendor Management) :
- Risk Assessment shall be performed for all the Vendors of API, KRM, KE, Primary Packaging Materials, and Printed PackagingMaterials once in a year by the concerned Site Quality.
-
- The outcome of risk assessment shall be shared with the Vendor Qualification Office at the latest by end of December for the current calendar year.
-
- Vendor Qualification Office shall prepare an Annual Vendor Audit Planner by consolidating data of Annual Risk Assessment received from all Sites.
-
- A copy of the Approved Audit Planner shall be shared with each Manufacturing Site and execution shall be from April to march (Financial Year).
-
- Risk-Based Approach for planning Vendor Audits shall be based on two primary principles which are:
-
-
- The evaluation of risk to cGMP status of Vendor and quality of material ultimately linking back to the protection of the patient.
-
-
-
- The level of effort, formality, and documentation of the risk assessment process should commensurate with the level of risk and should be based on scientific knowledge.
-
Risk Assessment Methodology under vendor management:
- The site shall create and maintain a list of all existing and potential Vendors of API, KRM, KE, Primary Packaging Materials, and Printed Packaging Materials for the assessment period.
-
-
- Identify the source of information of the Vendors and analyze the information to determine the risk of an individual Vendor.
-
- Classify the potential risks arising from the assessment of each category/parameter into four levels namely High, Medium, Low, and Negligible.
-
- Depending on the risk level of a parameter used for evaluation, a risk factor shall be assigned.
-
- By using the potential risk for each category and risk factors, a Risk Priority Number (RPN) shall be calculated (quantitatively).
-
- Risk Factors can be grouped into three categories as shown in the following table (Table E):
Table E: Types of Risk Assessment Categories
| Category | Typical parameters for assessment |
| Severity | The criticality of material and impact on end-product quality |
| Probability | Supply history of Vendor and status of Quality Systems of the Vendor |
| Detection | Possibility of detecting quality failures for a material and the stage at which detection is possible (e.g. incoming inspection, final testing, etc.) |
-
-
Severity:
- This category describes the criticality of material for the quality of the end product.
-
-
- Assessment for this category shall be done as per Table F.
Table F: Potential impact level of Category “Severity”
| Assessment Criteria |
Impact Assessment of risk level |
Risk Factor |
| Material under consideration is API or KRM used
for API manufacturing or Sterile Excipient |
High | 10 |
| Material under consideration is Primary or Printed PM | Medium | 8 |
| Material under consideration is non-sterile KE | Low | 4 |
| Material under consideration is other than KRM/other than KE/other than primary or printed PM | Negligible | 1 |
-
-
Probability of Occurrence:
- This category considers the past supply history (from a quality perspective), product SISPQ (Safety, Integrity, Strength, Purity, and Quality) requirement, compliance status, and state of quality systems of a Vendor.
-
-
- The risk criteria “compliance” classifies the product SISPQ requirement compliance and regulatory compliance status of the Vendor using all available information from the company’s quality management systems.
-
- Data for the parameter ‘Compliance’ can be taken from different sources, for example, the previous audits, assessment of information are provided by the Vendor in the Vendor questionnaire, etc.
-
- If the compliance status is unknown, the highest risk level shall be used.
-
- The vendor will be calculated by considering the Q Score of Vendor for the last three years.
-
- In case of a new Vendor or existing Vendor for new material where no previous Q Score is available, for impact assessment of this parameter, it will be considered as high risk.
-
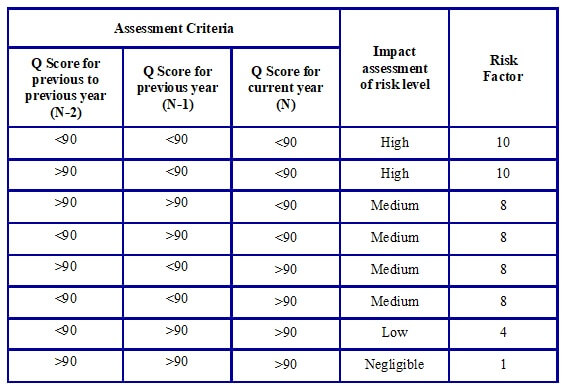
- Assessment for parameters “supply history of Vendor” and “compliance” shall be done as per tables G, H, and I respectively.
Table G: Potential impact level of Category “Supply History of Vendor”
-
- In the case of an existing Vendor with irregular supply of material, the assessment shall be done as per the following Table H.
Table H: Assessment criteria for irregular supply by existing Vendors
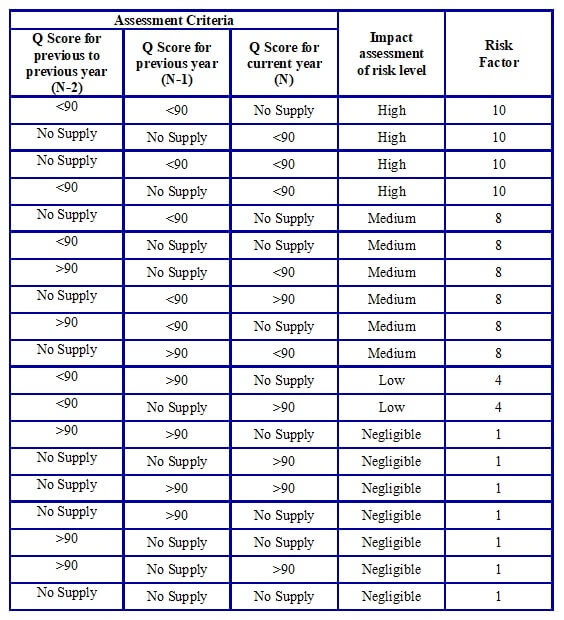
-
- In case there is no supply history for a particular material for the previous three years, if the Vendorhowever has been supplying other materials regularly from the same site, the assessment may be done based on the supply history of the other materials being regularly supplied by the Vendor from the same manufacturing site.
Table I: Potential impact level of Category “Probability of occurrence” and parameter “Compliance”
| Assessment Criteria |
Impact Assessment of risk level |
Risk Factor |
| Compliance status by company audit or an inspection by the competent regulatory authority (USFDA, EDQM, Japanese or Any European health authority,
WHO, TGA, Indian FDA, ANVISA, ISO, IPEC, etc.) available but older than 3 years or more for API and older than 5 years or more for KRM/KE/ Primary and Printed PM. |
High | 10 |
| Compliance status by company audit or inspection by the competent regulatory authority (USFDA, EDQM, Japanese or Any European health authority,
WHO, TGA, Indian FDA, ANVISA, ISO, IPEC, etc.) available but more than 2 years old for API and 4 years or more for KRM/KE/ Primary and Printed PM. |
Medium | 8 |
| Status of Compliance by company audit or inspection by competent regulatory authority available, more than 1 year old, but less than or equal to 2 years for API and more than 3 years old, but less than or equal to 4 years for KRM/KE/ Primary and Printed PM. | Low | 4 |
| The vendor is audited by the company in the last one year for API and the last 3 years for KRM/KE/ Primary and Printed PM. | Negligible | 1 |
-
- The total risk for category Probability shall be arrived at by averaging the risk factor of each parameter assessed under this category.
Total Risk (Probability) = {Risk factor (Supply History of Vendor)) + Risk factor (Compliance)} / 2.
-
- Detection: This category considers the Possibility of detecting quality failures for a material and the stage at which detection is possible and the assessment shall be carried out as per Table J.
Table J: Risk Assessment for detecting possible quality failure for material at various stages
| Assessment Criteria |
Impact assessment of risk level |
Risk Factor |
| Can be detected at in-process / intermediate stage / at finished product stage only | High | 10 |
| Can be detected during testing only but reduced testing performed | Medium | 8 |
| It can be detected at the receipt stage. No reduced testing performed, however, reduced sampling is done and vice versa. | Low | 4 |
| It can be detected at the receipt stage. No reduced testing / reduced sampling performed | Negligible | 1 |
-
-
Evaluating the Total Risk Arising from a Vendor:
- Evaluate the risks identified for all three categories (Severity, Probability, and Detection) for each individual Vendor.
-
-
- Calculate the vendor’s overall risk Priority Number (RPN) by multiplying the total risk of each category.
-
- Perform the risk assessment for each material and Vendor.
-
- In case of different RPN numbers obtained for different material/ material types by the same Vendor, the worst-case shall be considered for deciding the requirement of onsite audit of the Vendor.
-
- Perform the risk assessment for materials manufactured and supplied by any of the site(s).
-
- In the case of products that are manufactured for a customer, initially, the Vendors shall be approved based on the customer’s recommendation.
-
- Perform the annual risk assessment of such Vendors as per this SOP.
-
- Obtained the RPN values shall use for sorting Vendors according to their overall risk factor once in a year(preferably by the end of December).
-
Risk Control Evaluation and Audit Plan:
- Risk control evaluation shall involve focusing the scope of risk management by selectively reducing risk control for low-risk suppliers and increasing risk control for high-risk suppliers as per Table K.
Table K: Risk Control Evaluation and Audit Plan.
| Risk Priority Number (RPN) | Actions |
| Less than or equal to 64 (Low Risk) | No further actions required until the next risk assessment. |
| 65-256 (Medium Risk) | Paper-based audit |
| > 256 (High Risk) | All such Vendors shall be included in the annual audit plan for the onsite audit. |
-
- The risk assessment shall be reviewed annually.
-
- However, in certain cases, the risk of Vendor may be re-assessed earlier also on the acquisition of new assessment data or multiple rejections of a material.
5.0 ABBREVIATIONS USED IN SOP FOR VENDOR MANAGEMENT:
-
- ADD: Analytical development department
-
- API: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient
-
- BSE: Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy
-
- CC No: Change Control Number (Related – SOP for Change Control Management)
-
- DS: Drug Substances
-
- ERP: Enterprise Resource Planning
-
- FDD: Formulation development department
-
- GIM: Goods inward memo
-
- KE: Key Excipients
-
- KRM: Key Raw Material
-
- MPS: Master Product Specification
-
- MSDS: Material Safety Data Sheet
-
- NA: Not Applicable
-
- PVC: Poly Vinyl Chloride
-
- PVDC: Poly Vinylidine Dichloride
-
- R & D: Research and Development
-
- RS: Residual Solvent
-
- VIF: Vendor Information Form
-
- VQ: Vendor Qualification
-
- VQO: Vendor Qualification Office
-
- VSF: Vendor Survey Form
6.0 DEFINITION USED IN SOP FOR VENDOR MANAGEMENT :
-
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient(API) or Drug Substances(DS):
- Any substance or mixture of substances intended to be used in the manufacture of a drug (medicinal) product and that, when used in the production of a drug product, becomes an active ingredient of the drug product.
-
-
- Such substances are intended to furnish pharmacological activity or other direct effects in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease or to affect the structure and function of the body.
-
Approved Vendor:
- The manufacturer is supplying the material in routine and registered for the supply of specific material after the approval process.
-
Audit Objective:
- Describes the purpose and intent of the Audit.
-
Audit Observation:
- Results of the evaluation of the collected audit evidence against audit criteria.
-
Audit Planner:
- A document developed by the Vendor Qualification Office that indicates which Audit is to be performed during the financial year.
-
Audit Report:
- Document assembled by the Auditor and or the Audit Team which details the observations made during the Audit.
-
Audit Response:
- Document created by the Auditee that addresses corrective and/or containment actions taken in response to each Audit Observation.
-
Auditor/Lead Auditor:
- An individual qualified person (either from Corporate Quality Audit/QA/Qualified Personal {QP}) who is either a lead auditor or an auditor in the audit team to perform quality audits.
-
Batch/Lot:
- A specific quantity of material produced in a process or series of processes so that it is expected to be homogenous within specified limits.
-
- In the case of continuous production, a batch may correspond to a defined fraction of the production.
-
- The batch size can be defined either by a fixed quantity or by the amount produced in a fixed time interval.
-
Commercial Batch:
- Batch to be used for the production of Commercial-scale active pharmaceutical ingredients or manufacture of Commercial-scale drug products.
-
Component:
- Any ingredient intended for use in the manufacture of a drug product, including those that may not appear in such drug product.
-
Critical Rejection:
- Material rejection impacting Product Quality e.g. Assay, Microbial Tests, Impurity, etc.
-
Deregistered Vendor:
- A status of vendor which has been discontinued from the business based on quality/ commercial reasons.
-
Detection:
- The ability to discover or determine the existence, presence, or fact of risk.
-
Drug Product or Medicinal Product:
- Any substance or combination of substances which may be administered to human beings or animals to make a medical diagnosis or to restoring, correcting or modifying physiological functions in human beings or animals is likewise considered a drug or medicinal product.
-
Excipient:
- Excipients are components of a finished drug product other than the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and are added during formulation for a specific purpose.
-
Exhibit Batch:
- Exhibit batches are those which are manufactured and tested for regulatory filing using firmed up manufacturing instructions and specifications and test procedures.
-
- These are generally at least 10 percent of the size of the proposed production batch.
-
- These are also called ‘Bio-batches’ and they can be used for bio studies.
-
Existing Vendor:
- The existing Vendor is one that has already been qualified by any of the other Sites of the group of companies and is being considered for a New Material.
-
For-cause Audits:
- Audits that are conducted for a particular reason (s) e.g. audits done to investigate the cause(s) for critical rejection/complaints/recalls, import alert, etc.
-
Key Excipients (KE):
- Excipients which are claimed as critical in the respective process by R&D / FDD.
-
Key Raw Material (KRM):
- A raw material that is incorporated as a significant structural fragment of the structure of an API.
-
Key Reactant (KR):
- A raw material (other than Key Raw Material), which plays an active part in API / Intermediate synthesis.
-
Manufacture or Manufacturing:
- The complete cycle of Manufacture of an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient or Drug Product from the purchase of materials, dispensing of components through all processing, compounding, formulating, filling, testing, packaging, and labeling, the dispatch for sale or supply of the API or Drug Product.
-
Manufacturer:
- The producer company of the materials (API, KRM, Excipients, other Raw Materials, Packaging Materials, etc.) being procured.
-
New Vendor:
- New Vendor is one that has never been approved earlier for any material at any of the locations of the group of companies.
-
Non-Traditional API:
- Active substance materials that are not true APIs and where there is difficulty in getting the manufacturer of these starting materials to comply fully with GMP guidelines, usually due to the scale of production by the starting material manufacturer, etc.
-
Packaging Material or Packaging Component:
- Any material employed in the packaging of an API or Drug Product, excluding any outer packaging used for transportation or shipment.
-
- The term generally covers one or more of the following types:
-
- Primary packaging material, i.e. product contact parts such as containers, bottles, aluminum, PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride), and PVDC (Poly Vinylidene Dichloride) foils for strip and blister pack, poly bags, etc.
-
-
- Printed packaging material i.e., Label, leaflets, inserts, cartons, etc.
-
-
-
- Secondary packaging material, i.e. drums, etc.
-
-
-
- Other packaging material, i.e. shippers.
-
Paper-Based Audit:
- Review of filled Vendor technical mandate Documents and supporting documents, without conducting a physical on-site audit of the manufacturing facility.
-
Partial Manufacturing:
- Re-packaging or re-labeling activity or part manufacturing like micronization of a material is called partial manufacturing.
-
Provisional Approval (P):
- It is a status assigned to the vendor denoted as “P” for the first-time updates in the electronic or manual system based on a satisfactory review of mandate documents like VIF, TSE/BSE, and Residualsolvent declaration (as applicable).
-
Q-Info Record:
- The Q-Info record for every material – Vendor combination – shows Vendor status – Valid (with validity date and possible quantity level controls) – Non Valid (not re-validated, blocked, etc.).
-
Q-Score:
- A score allocated to each material-Vendor combination in the electronic system, representing material history and based on the outcome of the material disposition status i.e. approved/rejected or online rejection.
-
Risk:
- The combination of the probability of occurrence of harm, the severity of that harm, and the capability of the system to detect the harm.
-
Risk Assessment:
- A systematic process of organizing information to support a risk decision to be made within a risk management process.
-
-
- It consists of the identification of hazards and the analysis and evaluation of risks associated with exposure to those hazards.
-
- Control: Actions implementing risk management decisions to control risks.
- Evaluation: The comparison of the estimated risk of given risk criteria using a quantitative or qualitative scale to determine the significance of the risk.
- Identification: The systematic use of information to identify potential sources of harm (hazards) referring to the risk question or problem description.
- Management: A systematic process for the assessment, control, communication, and review of risks to the quality of the drug (medicinal) product across the product lifecycle.
- Reduction: Actions were taken to lessen the probability of occurrence of harm and the severity of that harm.
- Risk Review: Review or monitoring of output/results of the risk management process considering (if appropriate) new knowledge and experience about the risk.
- Severity: A measure of the possible consequences of a Risk.
-
Specification:
- A list of tests references to analytical procedures and appropriate acceptance criteria that are numerical limits, ranges, or other criteria for the test described.
-
- It establishes the set of criteria to which material should conform to be considered acceptable for its intended use.
-
- “Conformance to specification” means that the material, when tested according to the listed analytical procedures, shall meet the criteria.
-
Vendor:
- The vendor is an organization or a person that provides a material. It may be the manufacturer and/or supplier, providing material from a specific site.
-
-
Vendor “Under-Observation”:
- It is a status of the vendor issued an audit report or due to quality concerns.
-
Vendor Audit:
- Evaluation of the vendor’s manufacturing site, for the product of interest(s), for the understanding and application of the cGMP.
-
Vendor Qualification:
- Successful evaluation of Vendor’s ability and capability in meeting the company’s quality system requirements in relation to the criteria established for the material being sourced.
-



Pingback: API and Excipients - Receipt and Storage - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Supplier Selection and Qualification Standard Operating Procedures | Business Paper Example
Pingback: Quality Metrics - New FDA Guideline - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Stability Study SOP as per ICH Guideline - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: SOP for Drug Product Recall & Mock Recall - Pharma Beginners