Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Isolation and Identification of Microorganisms (Microbes).
Isolation and Identification of Microorganisms
1.0 PURPOSE:
-
- To lay down the Procedure for Isolation and Identification of Microorganisms.
2.0 SCOPE:
-
- This Standard Operating Procedure is applicable to the Microbiology Department at the pharmaceutical manufacturing unit.
3.0 REFERENCE:
-
- SOP for Aseptic Technique for Microbiological Testing.
-
- SOP for Environmental Monitoring Program.
-
- In House
4.0 RESPONSIBILITY:
-
- Officer or Executive of the Microbiology department shall be responsible for the preparation of new or revision of existing SOP.
-
- Head of the Department / Designee of respective areas & QA shall be responsible for reviewing the SOP.
-
- Site Quality Head and Head QA shall be responsible for the approval of SOP.
5.0 ABBREVIATIONS:
-
- CFU: Colony Forming Units
-
- ºC: Degree Celsius
-
- H2S: Hydrogen Sulphide
-
- IPA: Isopropyl Alcohol
-
- KOH: Potassium Hydroxide
-
- MR: Methylene Red
-
- NA: Not Applicable
-
- QA: Quality Assurance
-
- QC: Quality Control
-
- SCDA: Soyabean Casein Digest Agar
-
- SDA: Sabouraud Dextrose Agar
-
- SOP: Standard Operating Procedure
-
- TSI: Triple Sugar Iron
-
- VP: Voges Proskauer
-
- v/v: Volume by Volume
-
- % : Percentage
-
- +ve: Positive
-
- -ve: Negative
-
- DEFINITION:
-
- SOP: A written authorized procedure, which gives instructions for performing operations
-
- Colony-forming unit (CFU): Visible outcome of the growth of micro-organisms arising from single or multiple cells.
6.0 PROCEDURE- ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS:
-
-
Isolates from Water and Environment (Isolation of Microorganisms)):
-
-
- Isolate all the morphologically different colonies and identify them up to the genus preferably up to species level.
-
- Create a database (if required) for the cultures obtained from the water and Environment.
-
- Update the database as and when a new isolate is identified.
-
- Identify the predominant flora when the total microbial counts (microorganism) exceed alert and action limits in water or Environment.
-
- The characterization of the predominant flora shall be useful in investigating the excursions.
-
- Due to the physiological stress on the isolates, the organisms inherently may show up slightly different morphology. In this context, if an isolate is found morphologically different, the isolate shall be picked, and take a photograph of the colony for colony shape, elevation and Edge refer Annexure-4 (but not limited to) and identified.
-
- In case this organism is already identified (repeat isolate), then the database shall be updated accordingly, but the culture need not be preserved.
-
- Verify the growth promotion ability of the media using the isolates initially and record in Annexure- 3.
-
- The identified isolates shall be preserved for a period of one year using the seed lot technique and maintain the Annexure-2.
-
- Allot the number of seed lots of Environment and Water isolates as below.
-
-
- ISLCYYXXX
-
-
-
- Where:
-
-
-
- I – Isolates
-
-
-
- SLC – Seed Lot Culture
-
-
-
- YY- Last Two Digits of the current year
-
-
-
- XXX- Serial No. (Start from 001)
-
-
-
- For Example- ISLC16001
-
-
-
Isolates from the Non-Sterile Products (Oral Solid Dosage Forms) – (Isolation of Microorganisms):
-
-
- Isolate and identify the colonies if the total microbial counts exceed the action limits (Out of Specification results) in case of the finished products.
-
- Evaluate the isolates, summarize the identification profile and the recommendations to the Quality Assurance through an addendum to the OOS document.
-
- In case any of the isolates are identified as Specified Microorganisms, notify the Quality Assurance and Production department.
-
- Verify the growth promotion ability of the media using the Isolate initially and record in Annexure- 3.
-
- The identified isolates shall be preserved for a period of one year using the seed lot technique and maintain in Annexure- 2.
-
- Allot the numbers of isolates as per the above procedure defined.
- In the case of fungi obtained from monitoring, these isolates may not be identified always.
-
- However, the fungal isolates shall be used to verify the growth promotion ability of the media used for monitoring.
-
-
Isolation Procedure for Microorganisms :
-
-
- Media, Chemicals and Reagents.
-
Media (Isolation Procedure for Microorganisms) :
-
-
- Nutrient broth
-
-
-
- Simon’s Citrate agar
-
-
-
- Nitrate broth
-
-
-
- Urea Agar Base (Christensen)
-
-
-
- Triple Sugar Iron Agar
-
-
-
- Phenol Red Lactose Broth
-
-
-
- Mannitol Broth – Phenol Red
-
-
-
- Phenol Red Sucrose Broth
-
-
-
- Phenol Red Glucose Broth
-
-
-
- Starch Agar
-
-
-
- Nutrient Gelatin Medium
-
-
-
- Skim Milk Agar
-
-
-
Chemicals and Reagents (Isolation Procedure for Microorganisms):
-
-
-
- Gram Staining Kit
-
-
-
- Malachite Green Staining Reagent
-
-
-
- Methyl Red Solution
-
-
-
- Alpha naphthol, followed by 1 ml of 40% KOH
-
-
-
- Sulphanilic Acid and Alphanaphthalamine
-
-
-
- Zinc
-
-
-
- 3.0 % Hydrogen peroxide
-
-
-
- Oxidase disc
-
-
-
- Lacto Phenol Cotton Blue/Grocott Silver Stain/Hematoxylin/Eosin India ink.
-
-
- Pick the individual colonies from the previously incubated plates in which the growth is observed.
-
- Prepare the suspension of the colony in 10 ml of sterile peptone water.
-
- Take a loopful of prepared suspension and streak on the pre-incubated SCDA Plate.
-
- Streak the suspension in such a way to get a single isolated pure colony with its original phenotypic expression. Inoculate the culture into a slant also for seed lots of preparation.
-
- Incubate the plate at 30-35°C for 18-72 hours. In the case of fungal isolates, incubate the plate for 5 days.
-
- Plating of peptone water used for suspension should be done to confirm the sterility of the medium.
-
- Note down the colony characters of the isolate after sub-culturing as per the specimen format given in Annexure-1.
-
-
Identification of Bacterial Isolates (Morphological) – Identification of Microorganisms:
-
Gram Staining (Identification of Microorganisms):
-
-
- Conduct orientation checks like Gram nature and the shape and arrangement of the cells on the isolate. Perform the Gram staining as below.
-
- Prepare a thin smear of suspension on a clean, dry glass slide.
-
- Allow it to dry and fix by gentle heat.
-
- Flood with Gram’s Crystal Violet for 1 minute. Wash with tap water.
-
- Flood the smear with Gram’s Iodine and allow it to remain for 1 minute.
-
- Decolorize with Gram’s Decolourizer until the blue dye no longer flows from the smear. Wash with tap water.
-
- Counterstain with 0.5% w/v Safranin. Allow it to remain for 1 minute. Wash with tap water.
-
- Allow the slide to air dry or blow-dry and examine under the oil immersion objective.
-
- Gram-positive organisms should stain a bluish-purple color.
-
- Gram-negative organisms should stain pinkish-red color.
-
- Run the positive control during the Gram staining. For the positive control, use a reference culture of known Gram reaction.
-
-
Spore Staining (Identification of Microorganisms):
-
-
- Take a clean and dry glass slide and make it grease-free by passing it through the flame for 3-4 times.
-
- Take the growth of organisms to be identified by means of sterile nichrome wire loop/pre sterile loop on the clean glass slide and add a drop of purified water on agar culture.
-
- Spread evenly on the center of slide to prepare a smear.
-
- Allow to dry in air and gently pass it through flame 2-3 times for fixation of smear.
-
- Cover the smear with malachite green staining reagent.
-
- Heat the reagent gently by placing the slide on a warm hot plate or by exposing it to the flame of a Bunsen burner or water bath.
-
- Allow the reagent to evaporate for 2 to 3 min, more reagent may be added to prevent drying.
-
- Gently rinse the slide with purified water and spread the smear with 0.5 % Safranine for 30 second.
-
- Wash the smear with tap water, and blot dry gently prior to microscopic examination.
-
-
Shape (Identification of Microorganisms):
-
-
- The shape of bacteria may be of the following types.
-
-
Coccus (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
-
- Cocci: Single spherical.
-
- Diplococcic : Cocci that remain in pairs.
-
- Streptococci: Remain in chains of cells.
-
- Tetrad : Cocci remain in groups of four forming squares.
-
- Sarcinae : Cocci that remain in groups of eight forming cubes.
-
- Staphylococci : Cocci that remain in amorphous sheets or
-
-
Bacillus. (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
-
- Bacilli: Single rods, various shaped bacteria like a rod, tapered rod, staff, cigar, oval, curved.
-
- Diplobacilli (Paired rods): Bacilli that remain in pairs.
-
- Streptobacilli: Bacilli that remain in chains of cells.
-
- Vibrio: (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
- Comma Shape.
-
- Spiral: (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
- Spiral Shape.
-
- Motility (Identification of Microorganisms):
-
- Take a coverslip and put a small amount of petroleum jelly with the help of Sterile loop on each corner of the coverslip.
-
- Place one or two loops full of a 24 hours old broth culture in the center of the coverslip with the help of an inoculating loop.
-
- The depression slide is placed on the coverslip with the depression over the drop of fluid and quickly inverts the slide/coverslip.
-
- Examine with low power focus (10X and 40 X) on the edge of the drop (Use a minimum amount of light with unstained specimens).
-
-
Biochemical Identification (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
-
-
Indole Production (Identification of Microorganisms) :
-
-
- Prepare 1.0 % peptone water in test tubes and sterilize them by autoclaving at 121°C and 15 psi. for validated time.
-
- Aseptically inoculate the tube with the culture to be identified and incubate at 30-35°C for 48 hours.
-
- After incubation takes the tube and add 1 ml Kovac’s reagent (p-dimethyl amino benzaldehyde) and allow it to stand for one minute.
-
- Upon examination, if a Pink or Red color ring appears in the top layer of the medium it indicates a positive test with the breakdown of Tryptophan to Indole formation and no formation of color indicates the negative test.
-
-
Methyl Red Test (MR) – (Identification of Microorganisms) :
-
-
- Prepare a nutrient broth in test tubes as per SOP on media preparation and sterilize by autoclaving at 121°C and 15 psi. for validated time.
-
- Aseptically inoculate the tube with the culture to be identified and incubate at 30-35°C for 48 hours.
-
- After incubation takes the tube and add a few drops of Methyl Red solution to the culture tube and observe the result.
-
- Medium producing red color indicates the MR positive test and no formation of red color indicates the MR negative test.
-
-
Voges Proskauer Test (Identification of Microorganisms) :
-
-
- Prepare buffered glucose broth in test tubes as per SOP and sterilize by autoclaving at 121°C and 15 psi. for validated time
-
- Inoculate tube with the culture to be identified and incubate at 30-35°C for 48 hours.
-
- After incubation, add approximately 3 ml of Alpha Naphthol, followed by 1 ml of 40% KOH to the tube.
-
- Mix well and allow to stand for 15 minutes.
-
- Medium producing brick red color indicates the positive VP test and no color change indicates the negative VP test.
-
-
Citrate Utilization (Identification of Microorganisms) :
-
-
- Prepare the Simmon’s Citrate agar slants as per the SOP of media preparation.
-
- Streak Simmon’s Citrate agar slants with culture to be identified.
-
- Incubate plates at 30-35°C for 24-48 hours and observe after incubation.
-
- If the initial green color of media turns deep blue so it indicates the citrate utilization.
-
-
Nitrate Reduction (Identification of Microorganisms) :
-
-
- Prepare the nitrate broth tubes as per the SOP of media preparation
-
- Take the sterile tubes of nitrate broth and inoculate with a loop full of culture to be identified.
-
- Incubate tubes for 5 days at 30-35°C and observe after incubation.
-
- After incubation add 1 ml of Sulphanilic acid and 1 ml of Alphanaphtalamine in each nitrate broth culture tube.
-
- The reduction of nitrate to nitrite indicates the production of red color in the culture tube.
-
- After addition of Sulphanilic acid and alphanaphtalamine, if there is no production of red color, this indicates a negative test.
-
- Negative test is confirmed by adding a few particles of Zinc; the appearance of red color indicates that nitrate is still present and not reduced by the organism. If the solution does not change color the organism has reduced the nitrate through nitrate to nitrogen gas.
-
-
Urease Test (Identification of Microorganisms) :
-
-
- Prepare Christensen’s urea agar slant tubes as per the SOP for preparation and use of Microbiological Media.
-
- Take the sterile tubes of Christensen’s urea agar slant and inoculate with an inoculating needle by streaking the slant.
-
- Incubate tubes at 30-35°C for 24 hours and observed after incubation.
-
- Positive organisms utilize urea and make the media alkaline, producing a pink-red color.
-
- In the case of a negative test, urea agar slant and butt remains light orange.
-
-
Triple Sugar Iron Agar (TSI) – (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
-
- Prepare the Triple Sugar Iron Agar slants for stabbing as per the SOP of Preparation and use of microbiological media.
-
- Take the sterile tubes of TSI and inoculate with an inoculating needle by first stabbing the butt and then streaking the surface of slant.
-
- Incubate these tubes at 30-35°C for 24 hours and observe after incubation.
-
- If the butt color changes to yellow and slant color remain red, indicate Glucose fermentation.
-
- Color changes to yellow indicate Glucose, Lactose and/or Sucrose fermentation.
-
- If butt and slant color remain yellow, it indicates that no fermentation has taken place.
-
- H2S production is indicated by the presence of a black precipitate in butt.
-
-
Lactose Fermentation (Identification of Microorganisms) :
-
-
- Prepare the Phenol Red Lactose broth tubes as per the SOP for preparation and use of microbiological media.
-
- Take the sterile tubes of Phenol Red Lactose broth suspended with Durham’s tube.
-
- Inoculate the Phenol Red Lactose broth tube with a loop full of culture to identify.
-
- Incubate these tubes at 30-35°C for 24 hours and observe after incubation.
-
- Lactose fermentation indicates if the acid end product is produced and phenol red lactose turns yellow.
-
- If gas is produced along with the acid, it collects in the Durham’s tube as a gas bubble.
-
- If the Phenol Red Lactose broth remains unchanged and no acid or gas is produced, indicates no lactose fermentation has taken place.
-
- Mannitol Fermentation (Identification of Microorganisms) :
-
- Prepare the Phenol Red Mannitol broth tubes as per the SOP for preparation and use of microbiological media.
-
- Take the sterile tubes of Phenol Red Mannitol broth suspended with Durham’s tube.
-
- Inoculate the Phenol Red Mannitol broth tube with a loop full of the culture to identify.
-
- Incubate these tubes at 30-35°C for 24 hrs and observed after incubation.
-
- Mannitol fermentation indicates if the acid end product is produced and Phenol Red Mannitol turns yellow.
-
- If gas is produced along with the acid, it collects in the Durham tube as a gas bubble.
-
- If the Phenol Red Mannitol broth remains unchanged and no acid or gas is produced, indicates no Mannitol fermentation has taken place.
-
-
Sucrose Fermentation (Identification of Microorganisms) :
-
-
- Prepare the Phenol Red Sucrose broth tubes as per the SOP of preparation and use of microbiological media.
-
- Take the sterile tubes of Phenol Red Sucrose broth suspended with Durham’s tube.
-
- Inoculate Phenol Red Sucrose broth tube with the culture to identify.
-
- Incubate tubes at 30-35°C for 24 hours and observe after incubation.
-
- Sucrose fermentation indicates if the acid end product is produced and Phenol Red Sucrose turns yellow.
-
- If gas is produced along with the acid, it collects in the Durham’s tube as a gas bubble.
-
- If the Phenol Red Sucrose broth shall remain unchanged and no acid or gas is produced, indicates no Sucrose fermentation has taken place.
-
-
Glucose Fermentation (Identification of Microorganisms) :
-
-
- Prepare the Phenol Red Glucose broth tubes as per the SOP of preparation and use of microbiological media.
-
- Take the sterile tubes of Phenol Red Glucose broth suspended with Durham’s tube.
-
- Inoculate Phenol Red Glucose broth tube with a loop full of the culture to identify.
-
- Incubate tubes at 30-35°C for 24 hours and observe after incubation.
-
- Glucose fermentation indicates if the acid end product is produced and Phenol Red Glucose turns yellow.
-
- If gas is produced along with the acid, it collects in the Durham tube as a gas bubble.
-
- If the Phenol Red Glucose broth shall remain unchanged and no acid or gas is produced, indicates no Glucose fermentation has taken place.
-
-
Catalase Test (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
-
- Using a loop, pick a small growth of culture from a 24 hours old colony.
-
- Place the culture on a clean glass slide.
-
- Using a Sterile pipette or a dropper, place a drop of 3% Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) over the organism on the slide and observe for immediate formation of bubble.
-
- In the positive reaction Catalase test gives immediate bubbles if no bubble formation has taken place it means negative reaction for Catalase.
-
-
Starch Hydrolysis (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
-
- Prepare the Starch agar plates as per the SOP of preparation and use of microbiological media.
-
- Take the sterile Starch agar plates and inoculate with the culture to identify by streaking line on the agar surface.
-
- Incubate tubes at 30-35°C for 24 hours and observe after incubation.
-
- After incubation, add iodine to the surface of growth and observe the hydrolysis of starch.
-
- A positive reaction of starch hydrolysis indicates a yellow zone around the bacterial growth. If starch has not been hydrolyzed, the agar shall remain dark brown or blue/black in color.
-
-
Oxidase Test (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
-
- Take a sterile forceps and hold a test paper disc of the Oxidase (containing Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride).
-
- With the help of forceps touch the test paper onto an area of heavy growth to be identified.
-
- Observe the result immediately. Positive Oxidase test shows change of color from colorless to purple.
-
- If the color change takes place within 10 seconds test is positive, if the colour change takes place within 10 – 60 seconds it is delayed positive and more than 60 seconds it is negative.
-
-
Gelatin Liquefaction Test (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
-
- Prepare sterile Nutrient Gelatine stabbing tubes.
-
- Inoculate the tubes by stabbing of culture with the help of an inoculating needle.
-
- Incubate tube at 20-22°C and alternatively, incubate at 30-350C and then transfer the tube to a refrigerator or into cold water before observation.
-
- In positive test liquefaction of Nutrient Gelatine medium takes place and in negative test medium remains solid.
-
- Protein Hydrolysis (Casein) (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
- Prepare the Skim Milk agar plates as per the SOP of preparation and use of microbiological media.
-
- Inoculate Skim Milk agar plates with the culture using an inoculating needle.
-
- Incubate these plates at 30-35°C for 48 hrs and observed after incubation.
-
- If casein is hydrolyzed, there shall be a clear zone around the bacterial growth.
-
- If casein is not hydrolyzed, the agar shall remain white and opaque.
-
- Note down the observations as per the specimen format given in Annexure-1.
-
- Identify the isolate using a suitable identification method.
-
- Preserve the culture on a slant or plate till the identification is obtained.
- Record the results of identification in Annexure-1.
-
-
Identification of Fungal Isolates (Identification of Microorganisms) :
- Note down colony characteristics of fungal colonies developed on the media plates.
-
-
- Perform staining of the colonies using Lactophenol Cotton Blue as below:
-
-
- Place a drop of Lactophenol Cotton Blue reagent on a clean and dry slide.
-
-
-
- By using an inoculating wire, carefully tease the fungal culture into a thin preparation.
-
-
-
- Place a coverslip on the preparation and wait for 5 minutes.
-
-
-
- Observe under the microscope with low power for hyphal arrangement and morphology.
-
-
- Based on the Microscopy, identify the organism up to genus level by comparing it with characteristics given in the Annexure-4 (but not limited to).
-
- Record the results of identification in Annexure-1.
-
- In case of using the automated system for identification (up to species level) than the biochemical test not required.
-
-
Extent of Characterization of Isolates (Identification of Microorganisms)
- In all the above cases, the microbial isolates shall be identified based on the phenotypic characteristics as listed below.
-
-
-
- Culture- Colony morphology, colour, shape and size, pigment production
-
-
-
- Morphology- Cellular morphology, Gram reaction.
-
-
- In the case of any of the below cases, the isolates shall be identified by genotypic methods based on the investigation need.
-
- Any market complaint related to the microbial quality of the product
-
- Significant adverse trends in environmental and water monitoring.
-
- To support any investigation related to product quality.
-
-
Maintenance of Isolates (Identification of Microorganisms) :
- Follow the procedure detailed under ‘Seed lot preparation’ in the current version of SOP for revival and maintenance of the seed lots.
-
-
- Revive seed lots of environmental and water isolates as and when required.
-
-
Frequency (Identification of Microorganisms)
-
-
- Identification of Environmental and Water isolates on a yearly basis and if any new isolate is observed, GPT shall be conducted.
-
- In case any of the isolates is identified as Specified Microorganisms, notify the Quality Assurance, Production and Engineering Department.
7.0 ANNEXURES
Annexure 1: Identification of Microbial Isolates
A) Organism details:
| Source | |
| Location | |
| Date of Isolation | |
| Date of Testing | |
| Laboratory code No. |
B) Preliminary Observation:
| Test | Detail of observation |
| Name of Media | |
| Growth Temperature | |
| Colony color | |
| Shape of Colony | |
| Colony size | |
| Fluorescence | |
| Surrounding zone | |
| Other |
C) Photograph :
D) Identification Details of Bacteria.
- Morphological characteristics:
| Test | Detail of observation |
| Gram’s staining | |
| Spore staining | |
| Cell shape | |
| Cell size | |
| Arrangement | |
| Motility | |
| Mycelium | |
| Cell Photograph
|
|
- Biochemical characteristics:
| Sr. No. | Test | Results |
| 1 | Indole | |
| 2 | Methyl Red (MR) | |
| 3 | Vogus Proskauer (VP) | |
| 4 | Citrate utilization | |
| 5 | Glucose fermentation | |
| 6 | Lactose fermentation | |
| 7 | Sucrose fermentation | |
| 8 | Mannitol fermentation | |
| 9 | Nitrate reduction | |
| 10 | Urease | |
| 11 | Triple sugar Iron | |
| 12 | Catalase | |
| 13 | Starch utilization | |
| 14 | Oxidase | |
| 15 | Casein utilization | |
| 16 | Gelatin utilization |
Indole Production
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.____________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp______
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:_______________________________________________________
Results :_______________________________________________________
Methyl Red (MR)
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used ________________________Media Lot No.____________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp______
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:________________________________________________________
Results :________________________________________________________
Vogues Proskauer (VP)
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.____________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp______
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:_______________
Results:__________________________________________________________
Citrate utilization
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.____________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp______
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:________________________________________________________
Results :________________________________________________________
Glucose fermentation
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.____________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp______
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:________________________________________________________
Results :________________________________________________________
Lactose fermentation
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.______________________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp________________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:__________________________________________________________________
Results :__________________________________________________________________
Sucrose fermentation
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.____________________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp_______________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:__________________________________________________________________
Results :__________________________________________________________________
Mannitol fermentation
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No._____________________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp_______________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:_________________________________________________________________
Results :_________________________________________________________________
Nitrate reduction
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No._____________________________
Incubation: Time : From______________________ To_________________ Temp__________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:__________________________________________________________________
Results :__________________________________________________________________
Urease production
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.____________________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp_______________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:_________________________________________________________________
Results :_________________________________________________________________
Triple Sugar Iron Agar
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.____________________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp_______________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:_________________________________________________________________
Results :_________________________________________________________________
Catalase
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used______________________________ Media Lot No._____________________
Incubation: Time : From____________________ To_________________ Temp__________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:_________________________________________________________________
Results :_________________________________________________________________
Starch utilization
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used__________________________ Media Lot No.__________________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp_______________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:_________________________________________________________________
Results :_________________________________________________________________
Oxidase
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.____________________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp_______________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:_________________________________________________________________
Results :_________________________________________________________________
Casein utilization
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.___________________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp______________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:________________________________________________________________
Results :________________________________________________________________
Gelatin utilization
Date of Testing_____________________
Media used________________________ Media Lot No.____________________________
Incubation: Time : From________________ To_________________ Temp______________
Incubator Used ID No.:_______________
Observation:_________________________________________________________________
Results :__________________________________________________________________
Conclusion:
Annexure 1: Preservative Of Isolates Record
Annexure 3: Growth Promotion Test Of Isolates
| Date of Testing | ||||
| Name of Isolates | ||||
| Name of Media | ||||
| Media Sterilization Cycle No | ||||
| No. of Cells Inoculated (10-100 CFU) | ||||
| Temperature of Incubation | ||||
| Incubator ID | ||||
| Test Performed By | ||||
| Completed on | ||||
| Results: | ||||
| Plate I | Plate II | Average | % Recovery | |
Annexure 4
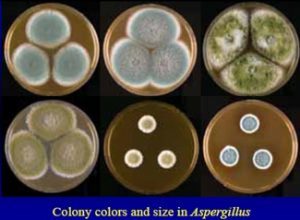
COLONY MORPHOLOGY, SHAPE & CELL ARRANGEMENT OF MICROORGANISMs



Pingback: Microbial Limit Test (MLT) of Non Sterile Product - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Media Fill Test - Aseptic Process Simulation in Micro - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Environmental Monitoring Guide - Non Sterile Facility - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Microbiological Media Management - SOP & Guideline - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Laminar Air Flow (LAF) - Operation, Cleaning and Qualification
Pingback: Microbial Culture Management SOP - Pharma Beginners