Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Handling and Management of Incident / Deviation under the Quality Management System (QMS) in a pharmaceutical plant.
Handling and Control Procedure for Incident / Deviation
1.0 PURPOSE:
-
- This Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) defines the key elements and requirements for reporting, documenting, evaluating, managing and resolving deviations/incidents from cGxPs approved specifications and/or procedures.
2.0 SCOPE:
-
- This SOP is applicable for incident/deviation from cGxPs, approved specifications and/or any established procedures including but not limited to-
-
-
- Batch Packaging Records (BPR),
-
-
-
- Facilities,

- Facilities,
-
-
-
- Storage,
-
-
-
- Distribution,
-
-
-
- Manufacturing,
-
-
-
- Testing,
-
-
-
- Packaging,
-
-
-
- Warehouse and distribution of drug products intended for use in humans, as well as drug substances at the pharmaceutical manufacturing plant.
-
-
- Note: 1. Events related to equipment or machine breakdown shall be recorded. Due to breakdown if the product is impacted then deviation shall be raised.
-
- This procedure is not applicable for out of specification, manufacturing, and analysis of trial batches, method development, and method transfer activities, OOS.
3.0 REFERENCES TAKEN FOR SOP OF INCIDENT / DEVIATION:
-
- In House
-
- SOP for Handling of Corrective and Preventive Actions
-
- SOP for Quality Risk Management
4.0 RESPONSIBILITY:
-
-
Quality Head/Designee shall be responsible for-
-
-
- The oversight and assessment of the deviation/incident.
-
- Reviewing and approving the deviation/incident.
-
- Approving requests for extension of timelines for deviation/incident closure.
-
- Timely resolution of all deviations/incidents.
-
- Assuring timely implementation of corrective actions and preventive action and ensuring corrective actions and preventive action is effective.
-
- Reviewing and approving the deviation/incident.
-
- Classification of the deviation/incident.
-
- Reviewing requests for extension of timelines for deviation/incident closure.
-
- Deriving appropriate CAPA and ensure adequate implementation of CAPA.
-
- The Disposition of impacted products/batches and/or releases other controls, based upon investigation conclusions of the deviations/incidents and associated corrections.
-
- Taking necessary action to notify customers and Regulatory Agencies about the deviation/incident, wherever applicable.
-
-
Manufacturing Head/ Designee shall be responsible for-
-
-
- Ensuring all manufacturing deviations are reported to the QA on the day of discovery.
-
- Ensuring that resources are available to support the deviation/incident and its resolution.
-
-
Quality control (QC) head /Designee shall be responsible for-
-
-
- Ensuring all deviations/incidents in the laboratory are reported to the QA on the day of discovery.
-
- Ensuring resources are available to support the deviation/incident and its plan assisting the QA as needed.
5.0 ABBREVIATIONS:
-
- ATP: Analytical Test Procedure
-
- BMR: Batch manufacturing record.
-
- CAPA: Corrective and Preventive Action
-
- CCR: Change Control Record
-
- CFT : Cross-Functional Team
-
- CQ: Corporate Quality
-
- EHS: Environmental health safety
-
- MSTG : Manufacturing Science Technical Group
-
- OOS : Out of Specification.
-
- PPID: Product Process Improvement and Development
-
- SISPQ : Safety, Identity, Strength, Purity, and Quality
-
- SME: Subject Matter Expert
-
- SOP : Standard Operating Procedure
6.0 DEFINITION OF TERMS USED IN SOP FOR INCIDENT / DEVIATION:
-
-
Acceptance Criteria:
-
-
- The product specifications and acceptance/rejection criteria, such as acceptable quality level and unacceptable quality level, with an associated sampling plan, that are necessary for making a decision to accept or reject a lot or batch (or any other convenient subgroups of manufactured units).
-
- The criteria, a system or process must attain to satisfy a test or other requirements.
-
-
Assessment:
-
-
- The act or process, of evaluating (e.g. extent, magnitude, position, impact or compliance level) of a process, system, project, action or activity.
-
-
Corrective and Preventive Action:
-
-
- A concept with current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) that focuses on the systematic investigation of root causes of unexpected incidences to prevent their recurrence (corrective action) or to prevent their occurrence (preventive action).
-
- Corrective Action: Action taken to eliminate the causes of an existing non-conformity, defect or other undesirable situation, in order to prevent recurrence.
-
- Preventative Action: Action taken to eliminate the cause of a potential nonconformity, defect or other undesirable situation, in order to prevent occurrence.
-
-
Cross Functional Team :
-
-
- Diverse team members (SME) typically comprised of heads from Quality, Manufacturing, Qualified Person, Regulatory, Laboratory or their qualified designees used to review and provide a disposition for the proposed deviation.
-
-
cGxP:
-
-
- cGxP is a general term that stands for current Good “x” Practice (x = Clinical, Engineering, Laboratory, Manufacturing, Documentation, Pharmaceutical, etc.).
-
- The titles of these Good “x” Practice guidelines usually begin with “Good” and end in “Practice”. cGxP represents the abbreviations of these titles where “x” a common symbol for a variable, represents the specific descriptor.
-
- Correction: Immediate action taken to resolve finding/issue.
-
- Critical Classification:
-
- Any departure from established standards that has caused or has high probability of causing adverse impact on product safety, quality, identity, potency or purity.
-
-
Deviation:
-
-
- Any departure (planned or unplanned) from approved procedures or records, including, but not limited to Standard Operating Procedure, Master Production Record, Batch Production Record, Standard Testing Procedure or the failure of a batch or any of its components to meet any of its specifications shall be documented and explained.
-
- Potential product quality impacting events shall be investigated and the investigation and its conclusions shall be documented.
-
-
Elimination:
-
-
- Errors Eliminate the possibility of error.
-
- This can be accomplished by eliminating the task. For example, eliminate mixing errors by purchasing pre-mixed materials.
-
- Eliminate recording errors by directly linking the measurement device to a printer.
-
- Event: Any unforeseen happening or unexpected occurrence.
-
- Incident / Unplanned Deviation– Owner: An individual responsible for initiating the event/incident investigation, determines root cause and implements corrections.
-
-
Incident/Unplanned Deviation:
-
-
- An unplanned or uncontrolled/unexpected GMP incident or deviation or an event in the form of departure from the designed systems or procedures at any stage of material receipt, manufacturing, packaging, testing, holding and storage of drug substance and it is Intermediate/Components due to system failure or equipment breakdown or human interventions and observed at a later time during execution, audit, etc.
-
- Initiator – Incident/Unplanned Deviation: An individual who initiates an event/incident record.
-
- Initiator – Temporary Change / Planned Deviation: Functional Supervisor or higher level person who initiates a Temporary Change or a Planned Deviation record.
-
- Investigation: A documented logical and/or scientific review of data related to all quality events that leads to the identification of the root cause and corrective and preventive action.
-
- Nonconforming Material: Material that does not meet specified acceptance criteria.
-
- Operating Group: Responsible Person(s) who execute Temporary Change/Planned Deviation along with other department member/team member.
-
-
Risk Assessment:
-
-
- A systematic process of organizing information to support a risk decision to be made within a risk management process.
-
- It consists of the identification of hazards and the analysis and evaluation of risks associated with exposure to those hazards.
-
- Root Cause:
-
- The underlying (fundamental) reason for a detected quality issue/failure (non-conformity, defect or other undesirable situation), which, if eliminated or corrected, will prevent recurrence of the problem for the same reason.
-
- Subject Matter Expert: An individual, who is educated, trained and/or highly experienced in a particular field or subject
-
- Task: Any activity identified as a part of executing a ‘Temporary Change’ or ‘Planned Deviation’. Tasks can be of two types, i.e., pre-requi (to be completed before execution of the temporary change or planned deviation) and non-pre-requi (can be completed concurrently with execution of the temporary change or planned deviation).
-
-
Temporary Change/ Planned Deviation:
-
-
- A temporary or interim need to deviate from a current approved requirement or to supplement, clarify or correct existing approved requirements. The term “temporary change/ planned deviation” is frequently used to describe a decision to carry out a process in a different way from which it is established in a SOP, Method or Manufacturing Batch Record.
-
- (e.g. a reprocess) due to an unforeseen event. Temporary change or Planned deviation need to be fully documented and justified. Usually, these are associated with onetime events or ‘Temporary Changes’ and the change control system must be used for permanent changes
7.0 PROCEDURE FOR HANDLING OF INCIDENT / DEVIATION:
-
-
Incident/ Unplanned Deviation:
-
-
- Any person (Initiator) can identify incident/unplanned deviation and shall initiate an incident/unplanned deviation record.
-
- It shall be reported to supervisor immediately and documented in the system on the day of discovery, but not later than end of next working day; a unique identification number shall be assigned to the record.
-
- Quality Assurance shall be informed within one (1) working day of discovery of the incident.
-
- QA shall assign the unique identification number for deviation as given below:
-
- It shall be in the format of “PB/ADV/YY/NNN”.
-
- Where,
-
- BS : Location Code (PB stand for Pharma Beginners)
-
- A : U or P (Where U is stand for unplanned/Incident and P is stand for planned.)
-
- DV : Deviation
-
- YY : Year of event Last 2 digit of year (20 for 2020 and so on.)
-
- NNN : Serial number of deviation.
-
- Every year, 3 digit serial numbers shall start from 001 and shall run continuously irrespective of the change in department code.
-
- e.g. First unplanned deviation of 2020 shall be PB/UDV/20/001, second planned deviation of 2020 shall be PB/PDV/20/002.
-
- QA shall make necessary entry in deviation log as per Annexure 2.
-
- QA shall issue the deviation form to initiator trough the document request form.
-
-
The Initiator shall provide the following information, but not limited to, as applicable:
-
-
-
- Short description
-
-
-
- Name of the department(s) involved
-
-
-
- Name of block to which event/incident belongs / area
-
-
-
- Event/incident category and sub-category
-
-
-
- Date discovered
-
-
-
- Description of the event observed, other related comments
-
-
-
- Results file/document shall be attached (if any)
-
-
-
- Product details- include other potentially impacted batch/batches event/incident
-
-
-
- Product stage, equipment involved (name and ID)
-
-
-
- Procedures/documents involved (SOPs, process documentation or product/material specifications)
-
-
-
- Systems involved
-
-
-
- Document affected electronic systems impacted (computer information Technology, hardware or software)
-
-
-
- Document related product/material test results
-
-
- Supplier(s) – identify material vendor(s) involved with the event event/incident batches under test, which are not yet released, shall be put on “Hold” status along with other batches identified for restriction.
-
- After initiating an incident/unplanned deviation, the initiator may cancel the record, if required.
-
- The cancellation shall be supported by valid justification / rationale and submitted to QA prior to closure of the deviation record.
-
- The Initiator shall describe details such as affected product, system, process and other relevant technical information while describing the incident/unplanned deviation.
-
- Speculation shall be avoided; any deductions or assumptions made shall be identified as such. Relevant questions to be considered include, but are not limited to, the following:
-
-
What is the potential impact of the incident/unplanned. deviation upon the safety, identity, strength, purity and quality of the finished product?
-
-
-
- In technical terms what is the incident/unplanned deviation about?
-
-
-
- When it was first observed?
-
-
-
- When and where did it occur?
-
-
-
- What is the extent or scope, including a description of all lot(s) and product(s) potentially impacted?
-
-
-
- When was the source of the incident/unplanned deviation last seen functioning properly (as expected)
-
-
-
- Who made the observation (include job title of individual)?
-
-
-
- A rationale for inclusion or exclusion of lots shall be documented in the report.
-
-
-
- All known events, such as the following, shall be documented in the report:
-
-
-
- Patient or worker safety
-
-
-
- Compliance with cGxPs
-
-
-
- Compliance with registration
-
-
-
- Incident/unplanned deviation from process validation
-
-
-
- Impact on product safety or efficacy
-
-
-
- Impact on product stability
-
-
-
- Effectiveness of previous corrective actions and notification requirements.
-
-
- A summary of any concerns associated with the incident/unplanned deviation not resolved and how these concerns influence the disposition of the lot, product or process shall be provided.
-
- Decisions concerning immediate correction(s) made shall be documented. Steps taken to prevent the incident/unplanned deviation from continuing shall be documented.
-
- The Initiator shall mention the name of the (Responsible Person), the Incident/Unplanned Deviation Owner and submits the record to the owner.
-
- The deviation owner may identify the cross functional team (CFT) comprised of individuals from affected or other s, resources external or Subject Matter Expert(s) in area(s) relevant to the deviation/incident.
-
- The deviation owner shall request additional information/details concerning the deviation/incident from the Initiator and CFT as necessary.
-
- Once the deviation owner receives all the details, he/she may initiate the correction for immediate action to correct the situation according to the
-
-
Initiation of Correction:
-
-
- The deviation owner shall initiate a correction and provide the following information, as applicable; the correction record shall be assigned a unique identification number assigned.
-
- Correction record number shall be assigned by QA.
-
- Correction record shall be assigned as prefix CR followed by “/ ” to reference Event/incident report number i.e. CR/ADV/YY/NNN/01.
-
- Where,
-
- CR is stand for Correction records followed by slash (/), followed by respective deviation no. Followed by (/) and then serial no of correction record.
-
- Short description
- Description of proposed correction
- Justification
- The deviation owner may withdraw the correction proposal and close the correction without implementation by providing proper justification summary and submitting to QA.
-
- If correction is required, the deviation owner shall forward the correction proposal to QA for review.
-
- QA shall review the proposal and may approve, if satisfactory or may seek additional information.
-
- Once approved by QA, the deviation owner shall implement the proposed correction.
-
- The impacted process due to incident/unplanned deviation shall be restarted only after QA approval of correction.
-
- However, in cases of emergency situations such as safety issues/immediate action required to prevent a crisis situation or further complications, QA approval shall be obtained retrospectively, as early as possible, but not later than the next working day.
-
- After implementation of the correction, the deviation owner shall submit the correction implementation record to QA for review.
- If QA review is satisfactory, the correction shall be closed.
-
- If the review is not satisfactory, QA shall return the record to the deviation owner with a justification summary.
-
- The deviation owner can provide additional comments and attach additional files/documents, if required.
-
- The deviation owner shall concur with all details and submit the deviation/incident for a risk assessment and deviation/incident criticality classification to the QA Head/designee.
-
Deviation / Incident Classification and Assessment:
- QA Head/Designee shall review the incident/unplanned deviation and may seek additional information and/or suggest changes. A summary of the proposed changes /required details shall be submitted to the deviation/incident owner.
- The deviation owner shall perform the changes and/or submit the additional information as requested to the QA Head/designee.
- QA may seek comments/consult of other departments, as warranted. Other departments, as identified, shall review and submit comments to
- Head QA /designee shall review comments from other departments and perform a risk assessment.
- QA shall determine any potential for adverse product impact and shall initiate appropriate control measures over impacted product(s), such as quarantine, suspension of relevant operations or other actions, as warranted, to address product quality or patient safety.
- A risk assessment must be carried out as per the written procedures mentioned in the current version of the respective SOP for Quality Risk Management.
-
QA Head/designee shall classify the incident/unplanned deviation as Critical/Major/Minor.
-
- The classification is dependent upon the possibility that it may impact Safety, Integrity, Strength, Potency or Quality of a Drug Product:
-
- Critical – Level – III: Any departure from established standards that has caused or has high probability of causing adverse impact on product safety, quality, identity, potency or purity.
-
- Major – Level – II : Any departure from established standards that may have an impact on the identity, quality, safety, purity, physical characteristics and efficacy of the product or process.
-
- Minor – Level – I : Any departure from established standards that may not have an impact on the identity, quality, safety, purity, physical characteristics and efficacy of the product.
-
- QA Head/designee shall enter the details of other impacted product/batches due to the incident/unplanned deviation in the relevant record.
-
- If impacted products/batches have already been released, the QA Head/designee shall take appropriate action, including but not limited to
-
-
- Customer/regulatory notifications,
-
-
-
- Withdrawal of product from distribution,
-
-
-
- Quarantine and so on of subject batches. (Summary report shall be attached to the incident/unplanned deviation record.)
-
-
- The incident/unplanned deviation number shall be referenced in all the records that are impacted, as deemed necessary.
-
All incidents/unplanned deviations shall be investigated according to the current version of the respective SOP.
-
- The QA Head/designee shall decide the extent of investigation required.
-
- The following guideline shall be followed to determine the extent of investigation:
-
-
- No impact/Likely impact/Direct impact on product, safety, identity, strength, purity and
-
-
-
- No impact on patient safety.
-
-
-
- Minor / Major / Significant GMP non-compliance
-
-
- The deviation owner shall review all investigations and root cause(s) for adequacy, correctness and completeness.
-
- If investigation reports are not satisfactory, the deviation owner shall request additional information and further investigation from the Responsible Person who performed the investigation.
-
- Upon the satisfactory root causes, QA shall intimate to other required department (if required).
-
- Upon satisfactory review, the root cause and proposed CAPA shall be submitted to the QA Head/designee along with a summary of the investigation. Any other correction/disposition of the affected product(s) shall be proposed as the individual proposing the CAPA can be the Responsible Person or any SME in the area in which the incident/unplanned deviation occurred.
-
- QA Head/designee shall review the investigation and root cause(s) for adequacy, correctness and completeness.
-
- If additional information is needed, QA may seek details from the deviation/incident owner.
-
- QA shall review the CAPA plan against the identified root cause(s).
-
- QA Head/designee shall evaluate the recommended CAPA and may approve implementation of the CAPA or discontinue CAPA with documented justification (refer to the current version of the respective SOP.
-
- Once QA approve the incident/unplanned deviation, CAPA records shall be initiated.
-
Closure of Incident / Unplanned Deviation – Disposition of Product:
- Incidents / Unplanned deviations shall be closed within forty-five (45) calendar days from the time that the incident/unplanned deviation is first discovered.
-
- If the incident/unplanned deviation cannot be closed in this period, the deviation owner must submit a request for extension as per attachment of timeline supported with adequate justification and rationale to QA for approval before the closure is due.
-
- This shall be submitted to Quality Head/designee for final approval.
-
- The deviation owner shall prepare an interim report that describes the action items that have been completed and those that are pending to accompany the request for extension.
-
- QA shall be notified when completion of a deviation/incident report exceeds assigned due dates.
-
- Overdue deviations/incidents shall be escalated to management and be included in the QRB meetings if deemed necessary.
-
- QA shall concur with the initiated CAPA and approve closure of the incident/unplanned deviation.
-
- Batches put “On Hold” shall undergo a final review by QA and shall be disposition accordingly.
-
- QA shall disposition impacted products/batches and/or releases other controls, based upon investigation conclusions and associated corrections.
-
- Ensure that all the CAPAs are submitted and are adequate before closure of the incident/unplanned deviation.
-
- QA shall take necessary actions to notify customer(s) / Regulatory about the incident/unplanned deviation, wherever applicable.
-
- QA shall ensure that a copy of the completed deviation/incident report is included in the appropriate document affected by the incident /unplanned deviation (i.e., Batch Production Record) and that references to all related documents are included in the record.
-
-
Temporary Change/Planned Deviation:
- A Temporary Change or a Planned deviation may be used for, but not limited to the following;
-
-
-
- Quality / Compliance improvements,
-
-
-
- Yield improvements,
-
-
-
- Batch Size changes,
-
-
-
- Equipment/Facility related issues.
-
-
- Examples include, but are not limited to changes in
-
-
- Equipment,
-
-
-
- Location/area,
-
-
-
- Processing step,
-
-
-
- Control limits,
-
-
-
- Packaging materials,
-
-
-
- Standard Test Procedures (STPs) and
-
-
-
- Sampling procedures.
-
-
- Temporary Change / Planned deviation are not to be used as a means to deviate from an approved requirement on a repetitive basis over time.
-
- Follow-up actions shall be taken to ensure that the use of this process is minimized and appropriate.
-
- A Temporary Change or a Planned Deviation are associated with one-time events and Change Control to Permanent Changes.
-
Initiation of Temporary Change / Planned Deviation:
- Any Responsible Person (henceforth, referred to as ‘Initiator’) may initiate a temporary change/planned deviation record and the record shall be identified with a unique identification number.
-
- The following information shall be provided as applicable:
-
-
- Short description of the temporary change / planned deviation.
-
-
-
- Reason for the temporary change / planned deviation.
-
-
-
- Name of the department
-
-
-
- Name of manufacturing block, area.
-
-
-
- Type of temporary change / planned deviation.
-
-
-
- Number of batches involved.
-
-
-
- Material code/description.
-
-
- Duration of temporary change / planned deviation shall not exceed ninety (90) calendar days from the date of its approval.
-
- Product stage, associated product / area / equipment.
-
- Associated documentation along with file attachment.
-
- Temporary Change/Planned Deviation Description:
-
- A complete and concise description of the planned event shall contain the following, but shall not be limited to:
-
-
- A statement of the temporary change / planned event (i.e. proposed versus existing).
-
-
-
- Address the elements of who (title only), what, when and where.
-
-
-
- Contain proposed instruction or a reference to approved instructions,
-
-
-
- Define interim controls required.
-
-
-
- The expected outcomes of the planned event.
-
-
- Define the period/number of batches, products, facility / equipment for which the temporary change or planned deviation shall be used or applicable.
-
- Provide the justification / rationale for the specified temporary change / planned
-
- Submit completed record to the QA Head/designee for review.
-
Review of Temporary Change / Planned Deviation:
- A cross-functional team (SME) that includes section heads from quality, manufacturing, regulatory, QA/ and any other department deemed necessary, shall review the temporary change/planned deviation, evaluate the risk associated with and will reject or approve the temporary change for further processing.
-
- The cross functional team shall:
-
- Confirm the information in the Temporary Change/Planned Deviation Form is complete.
-
- If additional information is needed, submit the summary of details needed to the Initiator.
-
- A risk assessment shall be conducted if required to evaluate the impact of the proposed change (refer to the SOP for Quality Risk Management).
-
- The Cross Functional Team shall reject the proposed temporary change/planned deviation and close it if the QA evaluation determines that there is an adverse impact on product quality. QA may seek additional comments/consults from other departments, as warranted.
-
- When the Cross Functional Team approves the temporary change/planned deviation action, the impacted specific products/batches shall be identified and control measures required determined (additional testing, market limitations and labeling as examples).
-
- The pre-requisite tasks identified shall be assigned before implementation of the temporary change/planned deviation.
-
- QA shall evaluate the need for an investigation and shall initiate one, if required, to identify the root cause for the factors that lead to the temporary change or planned deviation.
-
- The investigation shall follow the procedures as described in the current version of the respective SOP.
-
- Once complete information/details are available, the QA Head/designee shall evaluate and determine the potential impact of the change on the product and/or process quality.
-
- If it is acceptable, QA shall accept/approve the change, document the details accordingly and recommend it for implementation.
-
- QA shall assign the target end date.
-
Execution of Temporary Change/Planned Deviation:
- The Initiator (Functional Supervisor) shall:
-
- Ensure that all the tasks assigned (e.g. personnel training) as a prerequisite for the change implementation are completed.
-
- The initiator / functional supervisor shall identify the Operating Group responsible for execution of the temporary change/planned deviation after all pre-require tasks have been completed.
-
- The Operating Group may request approval to extend the due date of closure, number of batches to include, by submitting details in a summary report to QA shall review the request and if extension is acceptable, changes shall be made accordingly.
-
- The Operating Group shall submit the Temporary Change / Planned Deviation record to QA for review upon completion of execution.
- If the executed temporary change or planned deviation is found suitable for implementation on a permanent basis, then this shall be recommended for Change Control in the Temporary Change/Planned Deviation record.
-
- QA shall review to determine that all the pre-requi tasks, as identified, are completed. If additional information/details are needed, QA shall request them from the operating group.
-
- If the record is found to be satisfactory, QA shall close the Temporary Change / Planned Deviation record.
-
- QA shall evaluate the proposal for implementing the change as a permanent change and provide approval, make a request for further data or may reject it if not found suitable.
-
- Planned deviation or Temporary Change that will be made permanent shall be processed according to the current version of the respective SOP.
-
- QA shall take necessary actions to notify customer(s) about the temporary change / planned deviation, wherever applicable.
-
- QA shall ensure that a copy of the completed report is given in the appropriate document affected by the change, i.e. Batch Production Record , BMR, SOP, ATP, Protocol, etc.
-
Implementation of Pre-requisite / Non-prerequisite Tasks:
- The Initiator shall assign the task in consultation with QA for implementation with a unique identification number to the responsible person.
-
- Short description, Task category (pre- requisite and non-pre-requisite), Task start date, Task due date, Responsible Person to complete the task. Details of the proposed task, Comments, if any, attach supporting data, if any.
-
- The Responsible Person shall acknowledge the assigned task or reject if it is not justified.
-
- The Responsible Person shall complete the task and forward to the Initiator for
-
- The Initiator may request additional work from the Responsible Person if attached justification was incomplete or not satisfactory.
-
- If task verification by the Initiator is satisfactory, the task shall be considered as closed.
-
Review of Deviations Trends (Temporary / Planned and Unplanned):
- Quality Head / designee shall compile Deviation/Incident trends on a monthly basis for discussion/review/evaluation and shall include following:
-
- Data Trends: Evaluation of activity (e.g. volumes, percentage and repeat nature) based on on-going tracking as a function of time.
-
- Patterns: Assessment of product quality and process effectiveness based on logical groupings of data (e.g. Pareto Analysis).
-
- Comparative View: Analysis of Current quarterly trend with similar trend of previous review period to assess trends with potential impact on product quality.
-
- Effectiveness Analysis: Evaluations of initiatives taken to address issues raised previously, with recommendations of future activities related to Continuous Quality Improvement.
-
- Manufacturing Head and Quality Head or designee shall collectively analyse the deviation/incident trends and conclusions for further improvement at regularly scheduled management review meetings.
-
- Inadequacies identified during review shall be addressed with CAPA initiatives.
-
- QA shall be informed of the incident / deviations on the day of discovery, but not later than end of next working day.
-
- Each shall define the types of minor / major / critical incident categories that typically occur for the processes and procedures applicable to the facility and the criteria used for making this assessment.
-
- Incidents / Unplanned deviations shall be closed within forty-five (45) calendar days from the time that the incident/unplanned deviation is first discovered.
-
- QA shall establish and maintain a comprehensive system that assures all incidents/deviations are reported, thoroughly investigated, evaluated, managed, resolved, documented and trended.
-
- These steps can be accomplished through an electronic document management system or a manual, paper-based system, provided that the system allows incidents/deviations to be tracked and trended and allows appropriate follow up on any corrective and preventive actions and effectiveness checks.
-
There shall be regularly scheduled management review of incidents/deviations reports to identify trends or quality issues.
- QA shall inform Quality Head, Regional Quality Head and Corporate Quality Compliance Head or respective designee of any deviation or incident that may potentially have a multi- impact or require market action SOP for Product Recall.
-
- A written record of investigation related to the incidents/deviations shall be made and shall include conclusions and follow-up. Any meetings where investigations are discussed must be documented in writing as official minutes and included in the investigation.
-
- The system shall assure incidents/deviations are evaluated to determine whether they extend to other batches that might be implicated in the discrepancy or failure.
-
- Further assure incidents/deviations affecting batches already released are thoroughly investigated within seven (7) calendar days of the day of discovery in order to determine if there are any risks to patients from marketed product.
-
- The system shall assure a lot remains under quarantine and cannot be released if an open incidents/deviations exists on that lot.
-
- Extensions to incidents/deviations that are overdue shall be reviewed and approved by Quality Head/designee.
-
- Notification shall be sent to QA when completion of an incidents/deviations report exceeds assigned due dates.
-
- Conclusions and recommendations stated within incidents/deviations shall be managed by a consistent, clearly defined process with supporting justification, documentation and approval.
-
- Personnel responsible for identifying the root cause(s), making the conclusions and establishing corrective and preventive actions shall be designated and have appropriate training to perform their functions.
-
- QA shall review and disposition (reject/approve) the incidents/deviations report.
-
- QA shall track implementation of corrective actions and assess their effectiveness.
-
- The level of additional approvals required for an incidents/deviations report shall be based on the significance and risk associated with the incidents/deviations, however, the Quality Head/designee shall have final approval authority.
8.0 ANNEXURES:
Annexure 1: Unplanned Deviation /Incident Form.
| Date of Deviation | Reported By | Reported Date | |||
| Department | Documented By | Documented Date | |||
| Name of block to event/ incident belongs/area | Product stage | Involved equipment (Name and ID) |
|||
| Product / Material / System Details | Incident/ Unplanned deviation category | ||||
| Batch / Document / Equipment No. | Sub category | ||||
| Deviation Description: |
| Description of event observed, other related comments: |
| Target date | Revised target date |
| Investigation Team | |
| Subject Expert: | (Name) (Designation) (Sign & Date) |
| Department Head: | (Name) (Designation) (Sign & Date) |
| QA representative | (Name) (Designation) (Sign & Date) |
| Brief Review | ||||
| Discussion with concerned person : | ||||
| Document review: | ||||
| Procedure review: | ||||
| Equipment review: | ||||
| Manpower review: | ||||
| Material review: | ||||
| Systems review: | ||||
| Impacted document affected electronic systems review: | ||||
| Document related product/material test results review: | ||||
| Supplier(s) review: | ||||
| Others: | ||||
| Root cause (Assignable /Probable ): |
||||
| Impact analysis: | ||||
| Corrective Actions (pre-requisite for Batch Release) : | ||||
| Other Corrective Actions & Preventive actions :
CAPA No. |
||||
| CR No. | Short Description | Description of proposed correct | Justification | Closure status |
Annexure 2: Incident / Deviation Log.
Prepare the log in tabulated form with following contents..
-
- Date of issue
-
- Deviation No.
-
- Department
-
- Category-Planned/Unplanned
-
- Issue to
-
- Product
-
- Doc./Batch No/A.R No.
-
- Deviation Details
-
- Root Cause Identified/Not Identified
-
- Levels
-
- TCD
-
- Investigation No
-
- CAPA No.
-
- Status ( Open/Close/Cancel)
-
- Remarks
Annexure 3: Temporary Change/Planned Deviation Form.
For Deviation Form click here :Annexure 3 – Planned deviation Form
Annexure 4: Flow Chart for Temporary Change/Planned Deviation Reporting and Investigation.
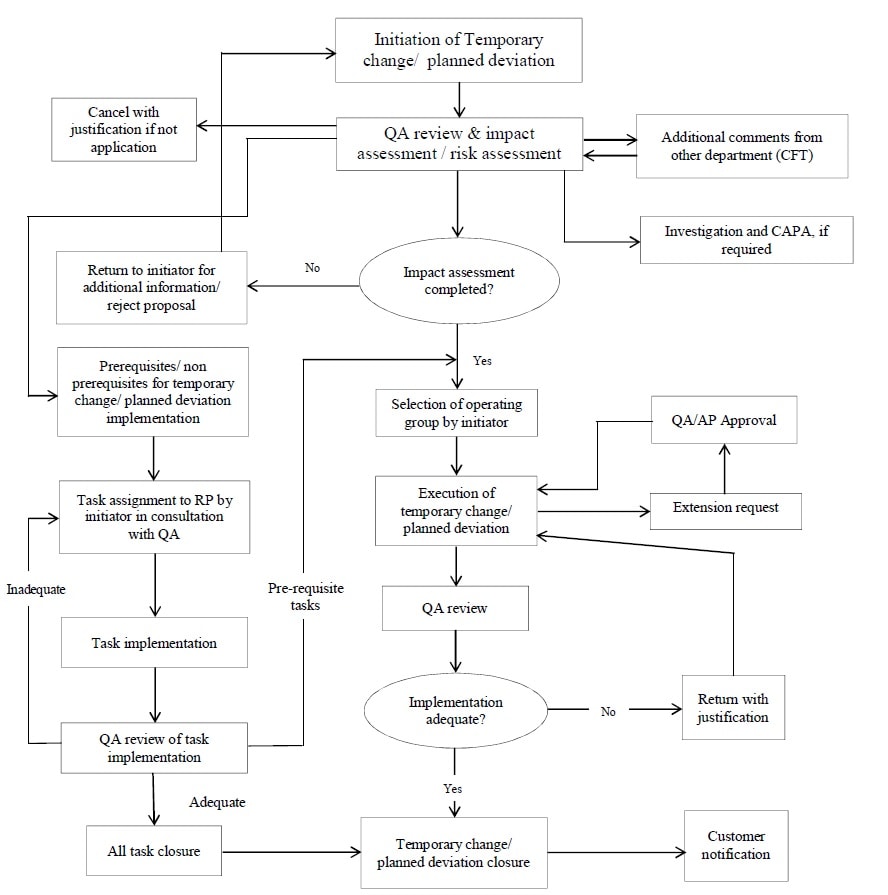
Annexure 5: Format for Target Date Extension of Deviation.
| Incident /Deviation No. | Investigation report No. | |||||
| Initial Target Completion date | ||||||
| Current status of Investigation : | ||||||
| Pending activities for Investigation : | ||||||
| Reason for Delay : | ||||||
| Justification for Delay : | ||||||
| Revised target Date | ||||||
| Prepared by
Sign & Date |
Reviewed by
Department Head Sign & Date |
Reviewed by
Quality Assurance Sign & Date |
Approved by Quality Head
Sign & Date |
|||
Annexure 6: Repetitive Event Trending and CAPA effectiveness evaluation.
| Date of Incident / Deviation | Incident /Deviation No. | Incident /Deviation
Level |
Product name | Batch No. |
| Incident /Deviation details | Root cause type | Action taken | CAPA | Remarks |
Annexure 7: Rolling Trends as Per Cause of Deviation.
Month-wise Incident Deviation Trending – For Format Click here :Format for Trending of Incident-Deviation
-
- Annexure 8: Flow Chart for Incident/Unplanned Deviation Reporting and Investigation.
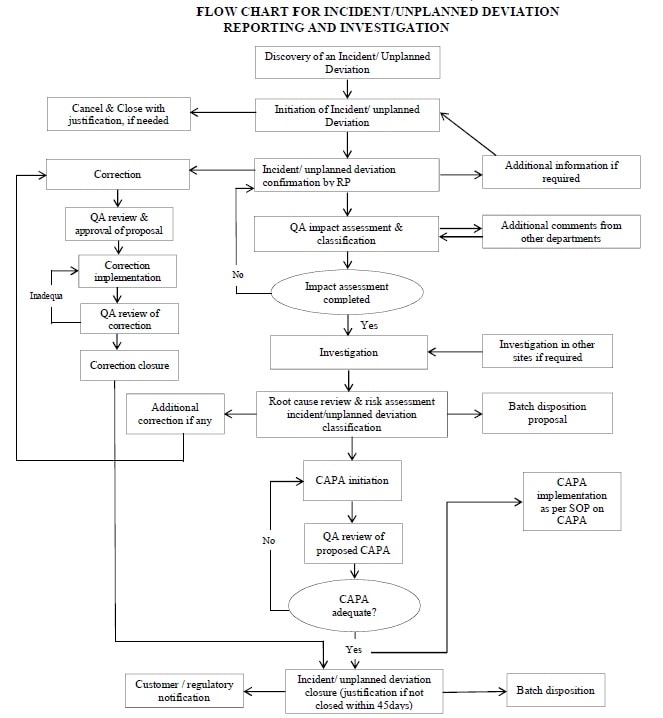
Annexure 9: Planned Deviation Information Form.
| Deviation Number | |
| Inform by | |
| Date |
|
| Time | From To |
| Brief Details of Change :
|
|
|
LIST OF PARTICIPANTS |
|||||
| Sr.
No. |
Name | Department | Designation |
Sign/Date |
|
| Summary of comment from other concern
Department: |
|
||||
| Reviewed by
QA Head |
|||||
NOTE: To be used only to inform Changes to concern persons within Location.
________________________________END_______________________________________



Pingback: Analytical Method Validation (AMV) - ICH Q2R1 Guideline - SOP
Pingback: Cleaning Validation Protocol -CV - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Deviation Process Flow? Best 238 Answer
Pingback: Out of Specification Result in Microbiology - Guideline - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Analytical Method Transfer (USP 1224) Guideline - Pharma Beginners